Nuclear Medicine Therapy
Unlock Exclusive Discount : Your Gateway to Premium Healthcare with Medsurge India Health Value Card.

Unlock Exclusive Discount : Your Gateway to Premium Healthcare with Medsurge India Health Value Card.

In nuclear medicine, a radiotracer is a small amount of radioactive chemical used to facilitate diagnosis.
The radioisotopic elements in radioactive tracers have replaced one or more atoms in a chemical compound. The major role of a radiotracer is to explore the mechanism of chemical reactions
Diagnoses, evaluations, and treatments of diseases are based on nuclear medicines. These include cancer, heart disease, gastrointestinal, endocrine, or neurological disorders, and other conditions. Consequently, they can detect disease at an early stage.
Nuclear medicine uses radioactive iodine (I-131) therapy to treat thyroid cancer, among other conditions.
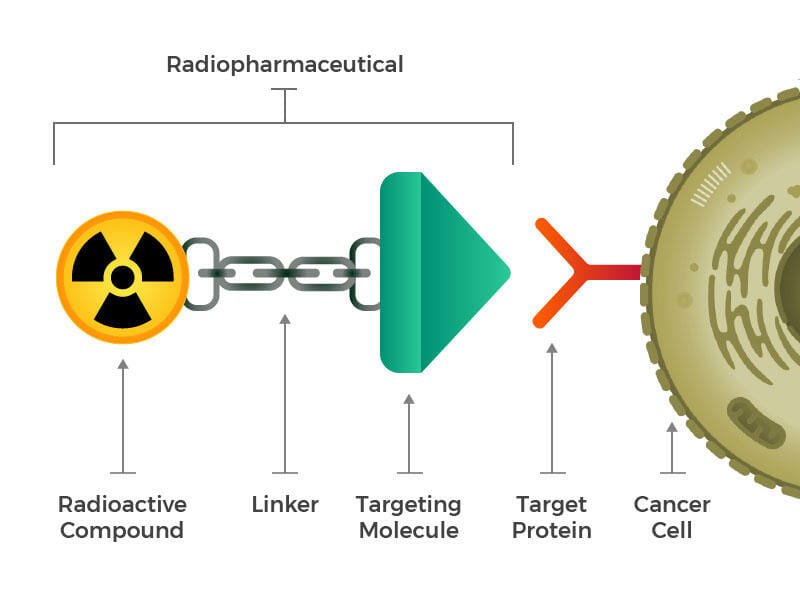
It is a special medical therapy that uses targeted radiopharmaceuticals elements to screen and treat tumors or cancer cells. Targeted pharmaceuticals contain radioactive particles called radioisotopes.
Therapeutic radioisotopes (radioactive particles) are combined with precision targeting compounds in targeted Radioligand therapy.
When a radioactive molecule is attached to a radioactive particle, it is referred to as labeling or radiolabeling in Nuclear Medicine Therapy.
As soon as the radioligand enters the bloodstream, it binds to the tumor, where it becomes a target for the radioisotope, which damages tumor cells, disrupting their ability to replicate or triggering cell death.
nuclear medicine therapy
Radioligand therapy can utilize a wide range of targeted ligands. A peptide can be a good example. This method is also known as Peptide Receptor Radiotherapy (PRRT).
It is possible for radioisotopes to emit different types of radiation, such as alpha, beta, and gamma, each with different properties and used for different clinical purposes.
Alpha and beta rays can not cover a long distance but they are strong in nature. Therefore, they are primarily used for treating disease since they can damage or destroy disease cells.
On the other hand, Gamma radiations have the capacity to travel far due to the highest energy and shortest wavelength. The detection of gamma rays is easily accomplished using specialized cameras and picture devices.
For Nuclear Medicine Imaging and Therapy, radioisotopes typically have very short half-lives, often only hours to a few days.
In this way, each dose of nuclear medicine is produced individually for each patient. Moreover, the shipping, handling, and administration of these medicines may require special procedures.
To ensure that the treatment is managed effectively, Advanced Accelerator Applications provides clinical development, regulatory approval, full commercial production, and logistical management.
By using our site, you agree to our Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy and Refund Policy. Medsurge India provides reliable healthcare information and treatment options to support informed decision-making. Our content is designed to support and complement the guidance of your treating doctor, helping you feel informed and confident throughout your healthcare journey. We also Accept International Payments.

Copyright © 2025 NSM ONLINE SOLUTIONS PRIVATE LIMITED. All rights reserved.