Microcephaly in Adults
Microcephaly, also known as Small Head Syndrome, is a condition that can lead to feelings of insecurity and low self-esteem in adults. This rare condition affects less than 0.1% of the population and is more commonly found in infants. However, some adults may develop the syndrome due to an underlying genetic disorder. Understanding the causes and finding ways to alleviate the symptoms are important aspects of managing this condition. In this blog post, we will explore its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options. Discover how early intervention and therapies can significantly impact the lives of individuals living with this condition.
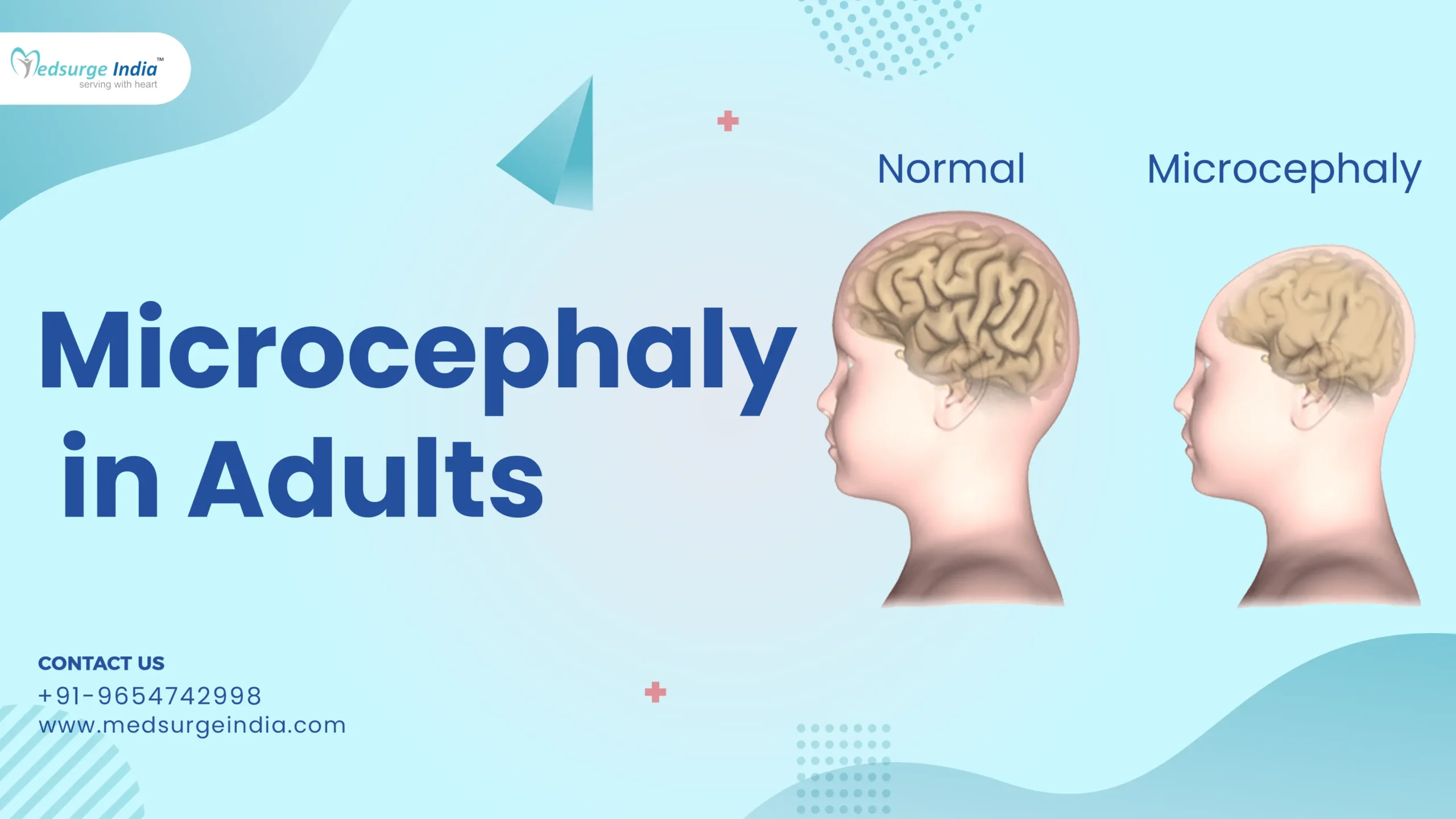
An Overview of Microcephaly
Microcephaly is commonly known as small head syndrome and it can affect both children and adults. It is broadly classified into two types, congenital or acquired microcephaly.
Congenital microcephaly refers to the condition where an individual is born with a small head size, which can be caused by genetic mutations or chromosomal abnormalities. On the other hand, acquired microcephaly occurs when the condition develops after birth, often as a result of brain infections, brain injury, neurodegenerative diseases, or specific medical treatments.
In adults, most cases of small head syndrome are acquired and can be attributed to causes such as trauma or exposure to certain toxins. The symptoms of microcephaly can vary depending on the underlying causes. These may include intellectual disabilities, developmental delays, difficulties with coordination and balance, as well as facial abnormalities. The appropriate treatment options for microcephaly depend on the specific underlying causes and may involve physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and medications.
Causes of Microcephaly in Adults
The cause of microcephaly in adults can be genetic conditions, brain injury, infections, environmental factors, and occasionally unknown causes This condition may be present at birth or develop later in life, emphasizing the importance of seeking medical guidance and obtaining an accurate diagnosis. Common causes are:
- Genetic abnormalities such as Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, or other chromosomal aberrations.
- Consequences of brain trauma such as head injury or stroke.
- Being exposed to toxic substances or radiation.
In some of the cases, the cause of microcephaly is unknown, and the condition is classified as idiopathic.
Symptoms of Microcephaly in Adults
Microcephaly in adults can result in various symptoms which can greatly vary depending on the underlying cause. The symptoms may include:
- Facial abnormalities.
- Speech difficulties.
- Seizures.
- Intellectual disabilities.
- Motor impairment.
- Developmental delay.
Diagnosis of Microcephaly
To diagnose microcephaly in adults, a physical examination is conducted first during which the head circumference is measured and compared to standard measurements for age, sex, and ethnicity. Microcephaly is defined as a head circumference that is more than two standard deviations below the mean. To confirm the diagnosis and find any underlying causes, more diagnostic testing could be carried out, such as:
- Genetic testing – To identify any types of genetic mutation or chromosomal aberration.
- Neurological examination – To evaluate cognitive abilities, physical abilities, and involuntary responses.
- Imaging tests – Imaging techniques, including CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds, can be employed to analyze the structure of the brain and identify any abnormalities.
- Blood tests – It can be utilized to ascertain the presence of infections or the exposure to harmful substances.
Treatment Approaches For Microcephaly in Adults
The treatment approach for Microcephaly may differ based on the particular case and the unique requirements of the patient. It is advisable to seek guidance from experienced neurologists to formulate an optimal treatment plan.
- Medications – Certain drugs may be recommended to assist in controlling symptoms such as seizures or behavioral problems.
- Surgery – In certain instances, surgical intervention may be advised to enhance the patient’s state.
- Physical therapy – Regular exercise can contribute to enhancing muscle strength, coordination, as well as overall function and mobility.
- Occupational therapy – It helps the patients to carry out their daily tasks, such as dressing and eating, despite their limited abilities.
- Speech therapy – Patients can enhance their communication and swallowing skills with the aid of this therapy.
Long-term Effects of Microcephaly
Microcephaly can significantly impact both the physical and cognitive abilities of an individual. The long-term consequences of this condition can vary greatly, depending on the severity of the condition and any accompanying medical complications.
Long-term physical effects include
- Delay of motor development.
- Delay in speech and language development.
- Elevated risk of seizures.
- Scoliosis and other spinal problems are more prevalent.
- Challenges with balance and coordination.
- The likelihood of hearing and vision impairment is increased.
- Respiratory infections are more likely to occur.
Long-term cognitive effects include
- Memory problems.
- Inability to pay attention.
- Communication and social interaction difficulties.
- Problems with reasoning, problem-solving, and abstract thought.
Also Read: Micro Laryngeal Surgery Cost In India






