
When it comes to addressing genetic disorders, bone marrow transplantation is a highly effective treatment option that has been shown to yield promising results. This process involves transplanting stem cells from a healthy donor into the patient’s body, which can help to replace damaged or diseased cells and promote the growth of healthy new cells. With its proven track record of success, bone marrow transplantation is an important tool in the fight against genetic disorders and offers hope to many individuals and families affected by these conditions.
This groundbreaking treatment option has the potential to alleviate symptoms, halt disease progression, and even cure certain genetic disorders. Here let us explore the basics of bone marrow transplantation and shed light on its efficacy, benefits, and considerations.
Understanding Genetic Disorders
Genetic disorders are caused by abnormalities or mutations in an individual’s DNA. These disorders can affect various aspects of a person’s health, ranging from physical and developmental disabilities to life-threatening conditions. While some genetic disorders have no cure, advancements in medical science, such as bone marrow transplantation, have revolutionized the treatment landscape.
What is Bone Marrow Transplantation
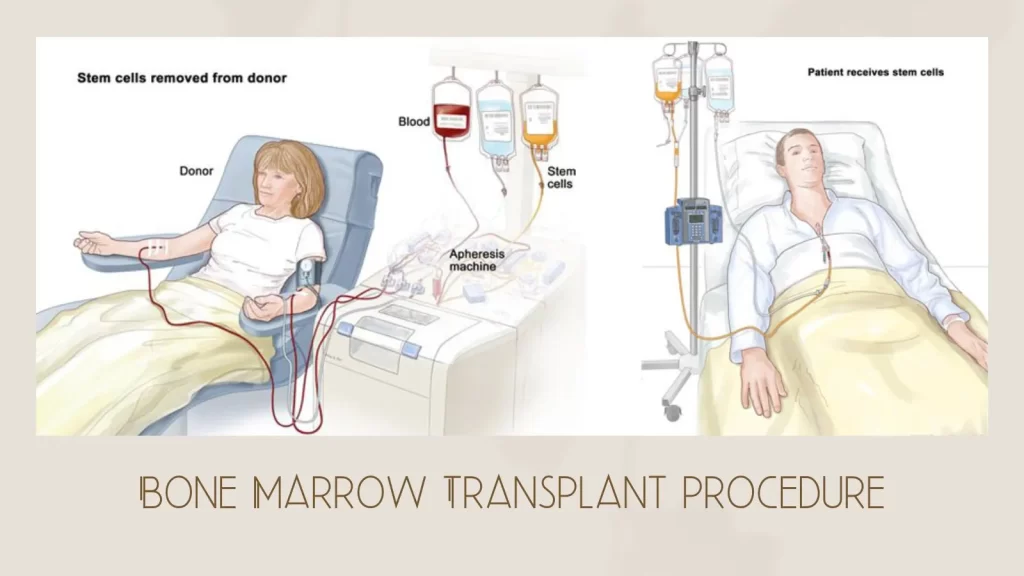
Bone marrow transplantation involves the transfer of healthy stem cells from a compatible donor to the recipient. These stem cells can be sourced from the bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood. The goal of the procedure is to replace the defective or malfunctioning stem cells in the recipient’s body with healthy ones, thereby restoring the body’s ability to produce normal blood cells and immune cells.
The Process of Bone Marrow Transplantation
1.Evaluation and Preparatory Phase
- A thorough evaluation is conducted to assess the recipient’s eligibility for transplantation.
- Compatibility between the recipient and potential donors is determined through human leukocyte antigen (HLA) testing.
- If a suitable donor is unavailable within the family, a search for an unrelated donor or alternative sources of stem cells may be initiated.
2.Conditioning
- Prior to transplantation, the recipient undergoes a conditioning regimen, which involves chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
- The purpose of conditioning is to destroy the recipient’s existing bone marrow cells and suppress the immune system, making way for the transplanted cells.
3.Transplantation:
- The healthy stem cells are infused into the recipient’s bloodstream through a catheter.
- The transplanted cells migrate to the bone marrow and begin producing healthy blood and immune cells.
Helpful: Bone Marrow Transplant Cost In India
Types Of Genetic Disorders Treated By Bone Marrow Transplant
Here are some common types of genetic disorders can be treated with bone marrow transplantation.
- Sickle Cell Anemia: Sickle cell anemia is an inherited blood disorder characterized by abnormally shaped red blood cells that can cause severe pain, organ damage, and other complications. Bone marrow transplantation offers a potential cure for sickle cell anemia by replacing the patient’s faulty bone marrow with healthy donor marrow. By providing a new source of healthy blood cells, this procedure can alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals with sickle cell anemia.
- Thalassemia: Thalassemia is another genetic blood disorder that affects the production of hemoglobin, the protein responsible for carrying oxygen in the blood. Individuals with thalassemia often require regular blood transfusions to manage their condition. However, bone marrow transplantation can offer a curative approach by replacing the defective bone marrow. This procedure can restore normal hemoglobin production and reduce the need for lifelong blood transfusions.
- Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID): Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) is a rare genetic disorder that affects the immune system, making individuals highly susceptible to infections. Bone marrow transplantation can be a life-saving treatment for SCID patients by replacing their faulty immune cells with healthy donor cells. This procedure can restore the immune system’s ability to fight off infections and provide these individuals with a chance at a normal, healthy life.
- Hurler Syndrome: Hurler syndrome is a rare genetic disorder known as a mucopolysaccharidosis that affects the body’s ability to break down certain sugars. This condition can lead to various physical and developmental abnormalities. Bone marrow transplantation can be used as a treatment option for Hurler syndrome by providing the patient with healthy cells that can produce the enzyme needed to break down these sugars. Although the procedure may not fully reverse the effects of the disorder, it can slow down its progression and improve the patient’s quality of life.
- Leukemia: Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. It is characterized by the overproduction of abnormal white blood cells, which can interfere with the body’s ability to fight infection and produce healthy blood cells. Symptoms of leukemia can include fatigue, fever, night sweats, and swollen lymph nodes. Bone marrow transplant is also used for treating leukemia.
Know More: Leukemia Treatment Cost In India
 Benefits and Efficacy of Bone Marrow Transplantation
Benefits and Efficacy of Bone Marrow Transplantation
Bone marrow transplantation offers several advantages for individuals with genetic disorders:
- Potential for a cure: In certain cases, bone marrow transplantation can provide a cure, as the transplanted cells can replace the faulty ones permanently.
- Symptom alleviation: Even if a complete cure is not achieved, bone marrow transplantation can significantly reduce symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Disease stabilization: For progressive genetic disorders, transplantation can halt or slow down disease progression, preventing further damage.
Conclusion
Bone marrow transplantation has emerged as a transformative treatment option for individuals with genetic disorders. It offers hope for a cure, symptom alleviation, and disease stabilization. While it is not without challenges, advancements in medical science continue to improve the success rates and accessibility of this lifesaving procedure. With ongoing research and the support of medical professionals, bone marrow transplantation holds the potential to transform the lives of countless individuals and families affected by genetic disorders.



 (1).png)