
About Radioembolization
Embolisation is a minimally invasive procedure in which blood arteries or abnormalities within blood vessels are occluded, or sealed off, to limit blood flow.Radiation treatment in India is done by using a specific type of energy known as ionizing radiation to destroy cancer cells and shrink tumors.
Radioembolization in India is used to treat tumors that originated in the liver or that have spread (or metastasized) to the liver from other places in the body. It is a palliative treatment, which means it does not cure the disease but rather slows its progression and alleviates symptoms. Patients who are not candidates for conventional treatments, such as surgery or liver transplantation, may benefit from the therapy. Radioembolization is a minimally invasive method that combines embolisation and radiation therapy to treat liver cancer in India.Tiny glass or resin beads comprising the radioactive isotope yttrium Y-90 are inserted inside the blood arteries which nourish a tumor. This cuts off the blood supply to the cancer cells and delivers a high dose of radiation to the tumor while preserving normal tissue. It can help people with incurable tumors live longer and have a better quality of life.
What is Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)?
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) is the most common primary liver cancer and the fourth leading cause of cancer death. It is an awful disease with life-threatening consequences. Hepatocellular carcinoma, if detected early, can be treated with surgery to remove the malignant tumor or with a Liver Transplant in India. additional procedures may reduce or slow down the tumor’s growth, relieving your symptoms. Cirrhosis of the liver and non-alcohol related fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are both linked to hepatocellular cancer. People with cirrhosis or NAFLD should be examined for symptoms of hepatocellular carcinoma on a regular basis.
Effect of Hepatocellular Carcinoma on your Body
Hepatocellular carcinoma may lead to liver failure with time. However, hepatocellular carcinoma may stop your liver from performing essential functions. Your liver, among other things,:
- Maintains the track of your body’s nutrients, transforming them into compounds that your body can use and storing and distributing them to your cells as needed.
- Collects hazardous substances and ensures that they are harmless or removed from your body.
- Encourages healthy blood flow by creating chemicals which help in blood clotting and eliminating microorganisms that cause disease.
Treatment for HCC
Several factors are considered while making treatment decisions for hepatocellular carcinoma, including tumor size, location, and morphology; comorbidity and/or extrahepatic disease; health condition; patient preferences; and the attending doctor’s experience and skill.
 The tumor microenvironment is gradually being recognised as playing an essential role in HCC carcinogenesis, with variables such as tumor and immune cell interactions, cytokines, and extracellular matrix playing important roles. Radioembolization Treatment for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in India, not only has a direct tumoricidal effect but also generates an immune response against tumor cells, resulting in immunogenic cell death.
The tumor microenvironment is gradually being recognised as playing an essential role in HCC carcinogenesis, with variables such as tumor and immune cell interactions, cytokines, and extracellular matrix playing important roles. Radioembolization Treatment for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in India, not only has a direct tumoricidal effect but also generates an immune response against tumor cells, resulting in immunogenic cell death.
What does the Equipment look like?
- X-ray equipment, a catheter, and microspheres, or microscopic glass beads filled with radioactive yttrium-90, are used in the procedure.
- X-ray guidance is often used during TARE Procedure in India.
- In this form of examination, a radiographic table, one or two x-ray tubes, and a video monitor are all commonly utilized. The process of turning x-rays into video pictures is known as fluoroscopy. Doctors use it to monitor and guide procedures. An x-ray machine and a piece of equipment positioned above the exam table create the images.
- A catheter is a long, thin plastic tube that is about the size of a “pencil lead.” It has a diameter of roughly 1/8 inch.
- The ionizing radiation is delivered by millions of glass beads, each smaller in diameter than a human hair and equal to about half a teaspoon full.
- Other equipment, such as an intravenous line (IV), an ultrasound machine, and sensors that monitor your heart rate and blood pressure, may be used during this process.
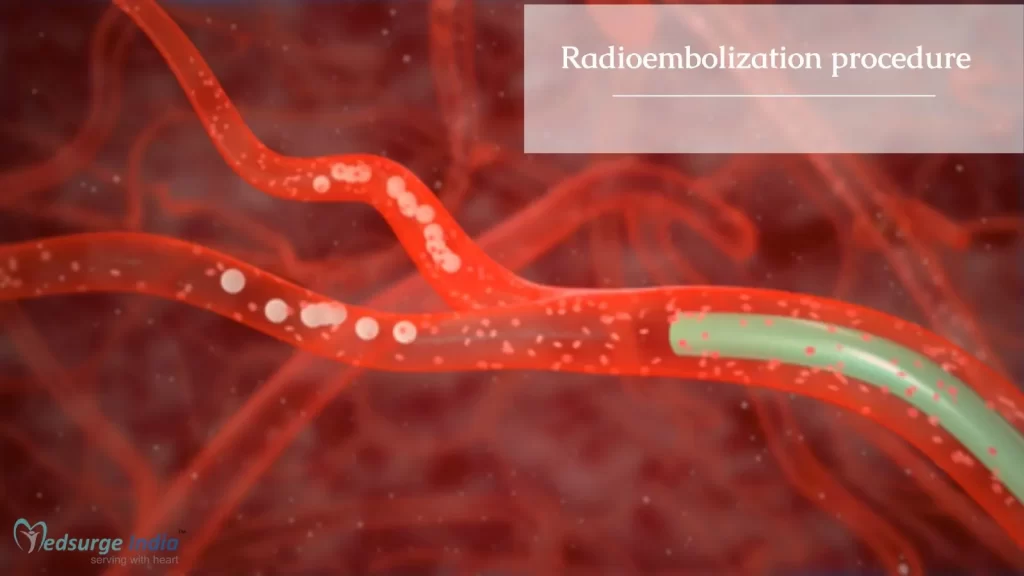
How does Radioembolization Therapy Works?
The interventional radiologist inserts a catheter through the skin into a blood artery and advances it to the treatment place using x-ray imaging and contrast material to see the blood vessels. The radiation-filled microspheres, also known as glass beads, are pushed through the catheter to the blood vessels that supply blood to the tumor.
Once embedded at the tumor location, the microspheres deliver a strong dose of radiation straight to the cancer cells. The microspheres will block blood flow to the tumor, depriving damaged cells of the oxygen and nutrients they require to flourish.
The liver is supplied with blood via two major blood arteries. The portal vein supplies around 75% of the blood supply to normal liver tissue, while the hepatic artery and its branches supply approximately 25%. When a tumor forms in the liver, the hepatic artery supplies nearly all of its blood supply. Because radioactive microspheres are supplied through the hepatic artery, they directly reach the tumor while sparing the majority of healthy liver tissue.
Over a two-week period, the radiation from yttrium-90 decreases gradually and finally disappears. The small microspheres do not cause any damage in the liver.
What are Radioembolization’s Limitations?
Radioembolization is not advised in cases of severe liver or renal disease, irregular blood coagulation, or bile duct blockage. Despite liver failure, radioembolization may be performed in tiny doses and throughout numerous procedures in some circumstances to try to minimize the effect on the normal liver.
Radioembolization is a treatment rather than a cure. Approximately 70 to 95% of patients will experience liver improvement, and depending on the kind of liver cancer, survival rates may improve. Multiple studies show that radioembolization can help as many as 95% of patients with colorectal metastases and 97% of patients with neuroendocrine tumors.
Best Nuclear Medicine Centre in India
- Indraprastha Apollo Hospital New Delhi
- Apollo Hospitals, Greams Road, Chennai
- Fortis Hospital Gurgaon
- Fortis Hospital, Bangalore (Bannerghatta Road)
- Amrita Hospital, Faridabad
- Global Hospital Mumbai



 (1).png)