Brain bleeding also known as a “brain hemorrhage” can occur as a result of an accident, a brain tumor, a stroke, or high blood pressure caused by congenital or other health conditions.
Brain bleeds can reduce oxygen delivery to the brain, increase intracranial pressure, and kill brain cells. If you are experiencing symptoms of a brain bleed, it is extremely crucial that you seek treatment as soon as possible.
For most cases of brain hemorrhage treatment in India, patients are taken to ICU in an emergency for medical management and close monitoring; however, a few cases will be operated on and the clot will be removed. Antihypertensive medications and diuretics are examples of medications given to such patients. External assistance is also provided, including IV fluids, hyperventilation, and anticoagulation reversal.
The cost of brain hemorrhage treatment in India is exceptionally low. The patient must spend 7 days in the hospital and 5 days out of the hospital. The total cost of treatment is determined by the diagnosis and facilities chosen by the patient.
What is Brain Hemorrhage?
When there is bleeding inside the brain or in the surrounding area, this is referred to as a brain hemorrhage. There are numerous causes of brain hemorrhage which include hypertension (high blood pressure), drug abuse, trauma, and blood vessel leakage. Depending on where the brain bleeds, there are three types of brain hemorrhage:
- An intracranial hemorrhage is a type of brain hemorrhage that involves bleeding inside the skull.
- Intracerebral hemorrhage occurs when there is bleeding inside the brain.
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage is a type of hemorrhage that occurs between the brain covering and the brain tissue.
A subdural hematoma occurs below the dura (tough covering) and an epidural hematoma occurs above the dura (tough covering) when blood clots between the brain and the skull.
A brain hemorrhage can occur when blood pressure against the artery walls continues to rise over time. This occurs as a result of high blood pressure and can result in arterial wall rupture. Prescription medications can also contribute to brain hemorrhage. Drug abuse weakens artery walls over time. Headache (pulsating pain caused by an aneurysm rupture), vomiting, nausea, numbness, changes in vision, difficulty swallowing, seizures, loss of consciousness; balance and coordination, difficulty in reading or writing, and lethargy are all symptoms of a brain hemorrhage.
What are the Symptoms of Brain Hemorrhage?
The symptoms of a brain hemorrhage vary depending on the area of the brain affected. Brain bleed symptoms, in general, can include:
- Tingling, numbness, or paralysis of the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body
- Headache (Subarachnoid hemorrhage causes a sudden, severe “thunderclap” headache)
- Vomiting and nausea
- Ambiguity
- Dizziness
- Seizures
- Swallowing difficulties
- Vision loss or difficulty seeing
- Balance Loss or coordination problems
- Neck stiffness and light sensitivity
- Speech that is abnormal or slurred
- Struggles in reading, writing, or understanding spoken language
- Changes in consciousness or alertness, fatigue, sleepiness, or coma
- Breathing difficulties and an abnormal heart rate (if bleed is located in the brainstem)
Read More – Craniotomy Surgery Cost in India
What are the Causes of Brain Hemorrhage?
There are several causes of brain bleeding, including:
- A fall, car accident, sports accident, or another type of blow to the head can all result in head trauma.
- High blood pressure (hypertension), can cause blood vessel walls to deteriorate and leak or burst.
- Fatty deposit buildup in the arteries (atherosclerosis).
- A blood clot that formed in the brain or travels from another part of the body to the brain, damaging the artery and causing it to leak.
- Aneurysm ruptures in the brain (a weak spot in a blood vessel wall that balloons out and bursts).
- Amyloid protein buildup within the brain’s artery walls (cerebral amyloid angiopathy).
- A leak is caused by improperly formed connections between arteries and veins (arteriovenous malformation).
- Disorders of bleeding or treatment with anticoagulant therapy (blood thinners).
- A brain tumor that presses against brain tissue and causes bleeding.
- Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, or the use of illegal drugs such as cocaine.
- Pregnancy or childbirth-related conditions, such as eclampsia, postpartum vasculopathy, or neonatal intraventricular hemorrhage.
- Conditions caused by abnormal collagen formation in blood vessel walls can cause the walls to become weak and rupture.
How the Diagnosis of Brain Haemorrhage is Done?
Diagnosis of a brain hemorrhage can be difficult because some people exhibit no physical symptoms. Doctors must conduct tests to determine the precise location of the bleeding in the brain.
Options for testing include:
- Evaluation of physical symptoms
- MRI or CT scan
- A lumbar puncture, also known as a spinal tap, is a procedure in which a doctor removes spinal fluid for testing using a hollow needle.
- Cerebral angiography is a procedure in which a doctor injects a dye into the brain and then takes X-ray images of it, with the dye highlighting abnormally shaped blood vessels in or near the brain.
- An electroencephalogram, a chest X-ray, and/or urinalysis may be performed.
- Complete vascular examination, complete blood count (CBC), and/or blood tests
- The cerebrospinal fluid that surrounds the brain is examined using a spinal tap.
- Conventional angiography may be used in some cases to detect an aneurysm or arteriovenous malformation.
Recommended Read: Hemorrhagic Stroke
Get Free Cost Estimation
Procedure
How Treatment of Brain Hemorrhage Done?
A medical emergency is any type of bleeding inside the skull or brain. Call an ambulance if you or a loved one has received a blow to the head or has symptoms of a brain bleed. It is absolutely important to get to a hospital emergency room as soon as possible to determine the cause of the bleeding and begin medical treatment.
If a stroke occurs, the cause (bleeding or a blood clot) must be identified so that appropriate treatment can begin. Prompt medical treatment can help limit brain damage, increasing your chances of recovery.
Brain hemorrhage is a life-threatening condition that may necessitate immediate medical attention and therapy. A neurosurgeon will diagnose the condition and perform the necessary tests to determine the best course of treatment based on their experience and training. It will be determined by the individual’s overall health and age, as well as the level of harm done to the mind and its location. The following are some of the procedures that may be performed as brain hemorrhage surgery in India:
Decompression Surgery: This treatment method is used to relieve the stress that the mind has as a result of some of the leading factors. An experienced neurosurgeon takes charge of the situation by removing the blood that has accumulated within the brain and repairing the damage caused by the blood vessels. As the pooled blood circulation is significantly reduced, draining the hematoma will help to relieve stress.
Craniotomy and Open Surgery: The doctor will remove a portion of the patient’s skull as well as perform an open operation to drain the hematoma and repair the ruptured blood vessel in this surgical method. This is a significant procedure performed when the hematoma is large or pressing against the brain stem, interfering with a number of critical brain functions.
Simple Aspiration: During this procedure, the surgeon will drill a hole in the patient’s skull and use a needle to drain the hematoma. It is relatively noninvasive in nature, but it can be difficult to pinpoint the exact location of the bleeding. As a result, the surgeon may not be able to completely drain the hematoma.
Endoscopic Evaluation: This method is similar to simple aspiration in that it will also require drilling a hole. However, instead of traditional surgical instruments, an endoscope (a tool with a tiny camera) can be used to locate the hematoma.
Stereotactic Aspiration: This procedure employs computed tomography (CT) to locate the hematoma and a technical suction tool to drain it. The person will be placed in a stereotactic head frame that will not allow him or her to move. It provides a high level of precision that would be impossible to achieve with other methods.
Helpful – Relevant questions to ask before you go for a NeuroSurgery
What are the Preventional steps Taken to Reduce the Risk of Brain Bleeding?
You can reduce your risk by doing the following:
- Maintain normal blood pressure.
- Reduce your cholesterol level.
- Get rid of excess weight.
- Limit your alcohol consumption and quit smoking.
- Maintain a healthy diet.
- Exercise on a regular basis.
- If you have diabetes, you should keep your blood sugar levels under control.
What Recovery You can Expect after Brain Hemorrhage Surgery?
Bleeding inside the brain not only deprives the brain of oxygen and kills brain cells, but also prevents nerve cells from communicating with the parts of the body and the functions they control. This causes memory, speech, and movement problems in the affected area.
A brain bleed can have long-term consequences depending on the location of the hemorrhage, the extent of damage, and your age and overall health. Among these effects are:
- Inability to move a portion of one’s body (paralysis).
- Numbness or weakness in a specific area of the body.
- Swallowing difficulties
- Loss of vision
- Difficulty in speaking or understanding the words spoken or written.
- Confusion, memory loss, or poor decision-making.
- Personality shifts and/or emotional challenges
- Seizures.
- Headaches.
However, with time and dedication to rehabilitation (physical, occupational, and speech therapy), you can regain some of these lost functions. This is especially true if your overall health is good.
Unfortunately, some patients who remain in a coma or have been severely paralyzed as a result of an intracranial or cerebral hemorrhage may require long-term care in a nursing home. Many patients do not survive the initial bleeding event, depending on the type, location, and extent of the brain bleeding.
Remember, the sooner you get to the emergency room if you suspect a brain bleed, the better your chances of survival. The time between the onset of symptoms and the onset of a bleed, as well as the time between the onset of a bleed and the confirmation of a bleed, are critical. The quicker a brain hemorrhage is discovered, the faster a treatment decision can be made. Don’t be quiet and reserved. Allow a medical professional to determine whether you have a brain emergency.
The Most Important Frequently Asked Questions
The Most Important Frequently Asked Questions About Brain Haemorrhage Treatment:
Q: How do I understand if I have a brain haemorrhage?
A: There are numerous symptoms that will allow you to know in case you own a brain haemorrhage. Be aware of these hints. You may experience severe headaches, vomiting, nausea, delirium, confusion, lethargy, sleepiness, apathy, lack of awareness, loss of equilibrium, difficulty in swallowing, difficulty in your speech abilities, etc.
Q: What complications can a brain haemorrhage cause?
A: The brain needs oxygen for working efficiently. The positioning of this haemorrhage will ascertain if there’ll be complications. A few of the complications could include seizures, psychological difficulties, depression, schizophrenia, fatigue, vision loss, stroke, or premature death.
Q: How can I prevent brain haemorrhage?
A: There are lots of risk factors that activate brain haemorrhages, thus minimizing them might help in preventing a brain haemorrhage. You are able to quit smoking, use drugs, drive, and treat your hypertension.
Q: Why are anti-epileptic drugs given while treating brain haemorrhage?
A: Together with the operation, your physician may prescribe several medicines. If the physician suspects that you may have seizures, he/she could prescribe you anti-epileptic medication.
Q: Is it normal to be more sensitive to noise?
A: Many individuals have reported that they feel sensitive to noise that’s rather tricky to deal with at times. Regular sounds would contain discussions, festival parties, television, etc.
Q: Will it be safe for me to have sex after the surgery?
A: A lot of individuals would experience small nervousness whenever they return to their regular sexual life. For a few the libido is going to be decreased. You may also experience stress if the bleeding happened when you’re having sex. Should you feel prepared, it’ll be fine for you to take part in sexual activity. However, that might not be permitted for at least a couple of weeks. Your odds of having a brain haemorrhage won’t grow with having sexual intercourse.
Q: Is it safe to be pregnant?
A: After treatment, the majority of the folks can get pregnant. It’s ideal to speak with your doctor concerning this if you aim of becoming pregnant.
Q: What is the recovery time after brain haemorrhage surgery?
A: Patients are typically discharged from the intensive care unit following a couple of days of the operation. It typically takes approximately 4-6 weeks to completely recover from the operation.
Q: Is it okay to fly after the surgery?
A: You will need to spend a sufficient quantity of time until you have completely recovered. After recovery, it’s fine to fly from one spot to another. However, it can turn up to be tiring for you as you will need a good quantity of rest after the procedure.
Q: How soon will I be able to drive?
A: The answer to this question will be different from one patient to another. You might need to wait around for about two weeks to begin driving. However, for complicated procedures, you may need to wait for more. Consult with your doctor about this to get a precise answer.
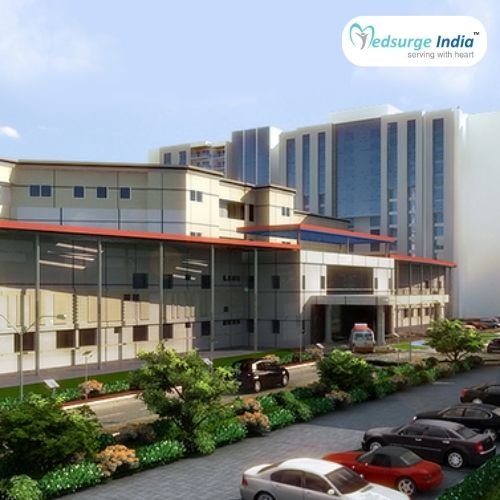
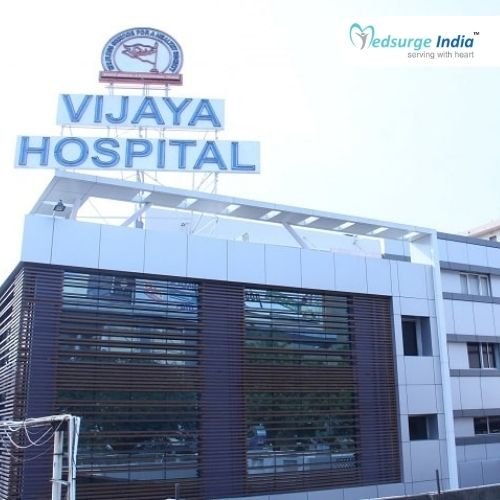
Top Hospitals for Brain Haemorrhage Surgery in India
Top Doctors for Neurology And Neurosurgery
Dr. Kiran M
Senior Consultant
Experience: 19 years of experience
Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences and Research Centre, Kochi
Bangalore, India
Dr. Siddhartha Ghosh
Senior Consultant , MBBS, MCh
Experience: 27 years of experience
Chennai, India
Dr. Tapas Chatterjee
Consultant
Experience: 18 years of experience
Calcutta Medical Research Institute, Kolkata
Kolkata, India
Dr. Priyank Patel
Consultant
Experience: 12 years of experience
Apollo Spectra Hospital, Mumbai
Mumbai, India
Dr. Khushbu Goel
Consultant
Experience: 14 years of experience
Manipal Hospitals Dwarka, Delhi
New Delhi, India
Dr. Mathew Abraham
Senior Consultant , MBBS, MD, DM
Experience: 33 years of experience
Kolkata, India
Dr. (Col.) Joy Dev Mukherji
Director
Experience: 40 years of experience
Max Super Speciality Hospital, Saket
New Delhi, India
Dr. Madhusudhan B K
Consultant
Experience: 9 years of experience
BGS Gleneagles Global Hospitals, Bangalore
Bangalore, India
Dr. Vivek Vaid
Director
Experience: 14 years of experience
Fortis Escorts Hospital Jaipur
Jaipur, India
Dr. Umesh Srikanth
Consultant
Experience: 11 years of experience
Aster CMI Hospital (Hebbel) Bangalore
Bangalore, India
Dr. Rupant Kumar Das
Consultant
Experience: 21 years of experience
AMRI Hospital, Kolkata (Dhakuria)
Kolkata, India