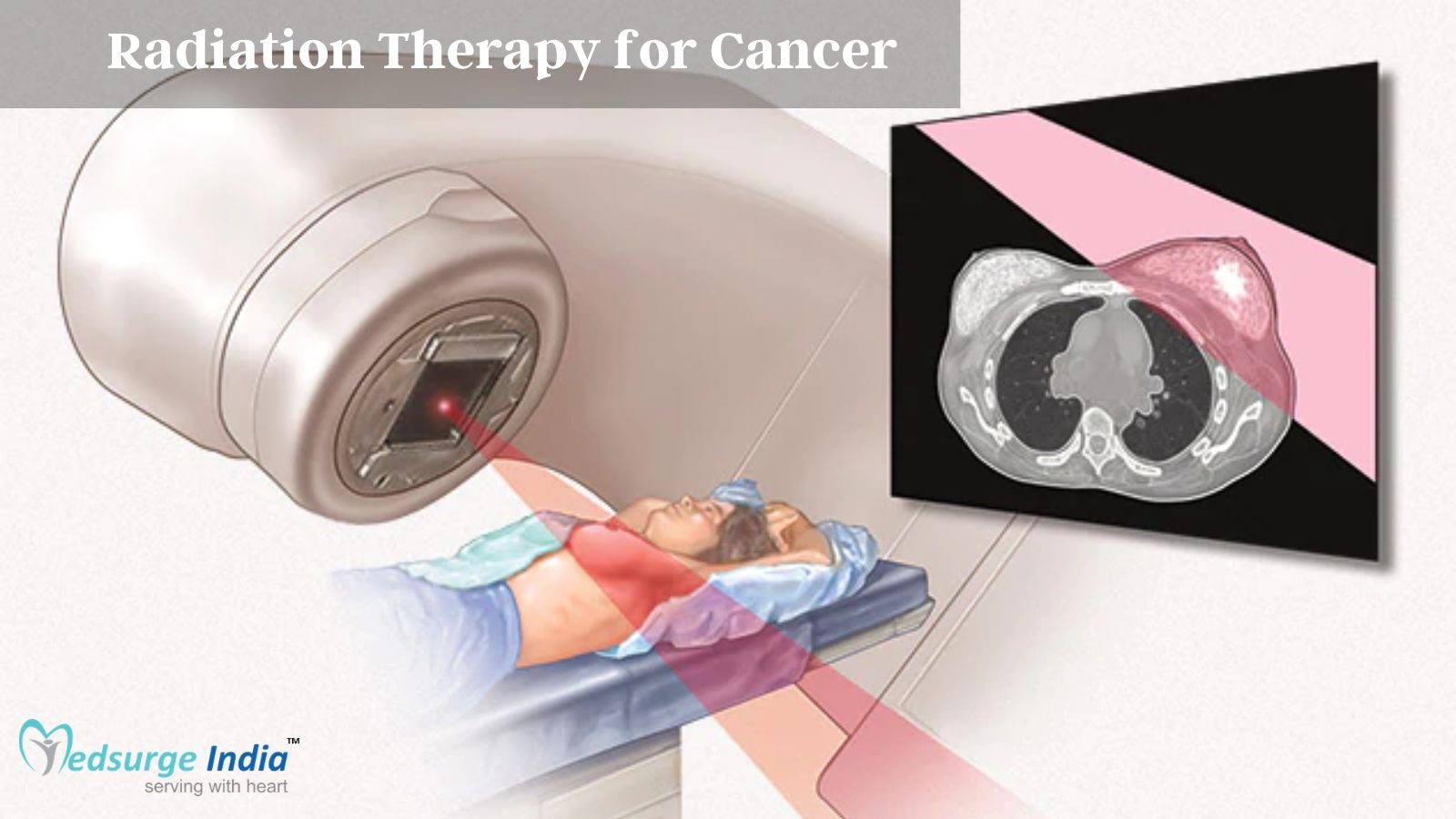
One of the most common Types of Cancer Treatment is Radiation Therapy in India. It pinpoints and destroys cancer cells using high-energy X-rays. Cancer cells are damaged by radiation, forcing them to stop replicating.
Radiation Oncologists in India are doctors who specialize in radiation therapy. Your radiation oncologist will decide if you would benefit from radiation therapy. If this is in fact the case, they will decide the optimum type of radiation therapy for the type of cancer you have. They also create the radiation therapy plan, including the radiation dosage that will target cancer cells while leaving healthy tissue alone.
Radiation Therapy in India is used to treat almost all types of cancer. In fact, radiation therapy is used in the treatment of more than half of all cancer patients. Radiation therapy may also be used to treat non-cancerous diseases. This includes non-cancerous tumors known as Benign tumors.
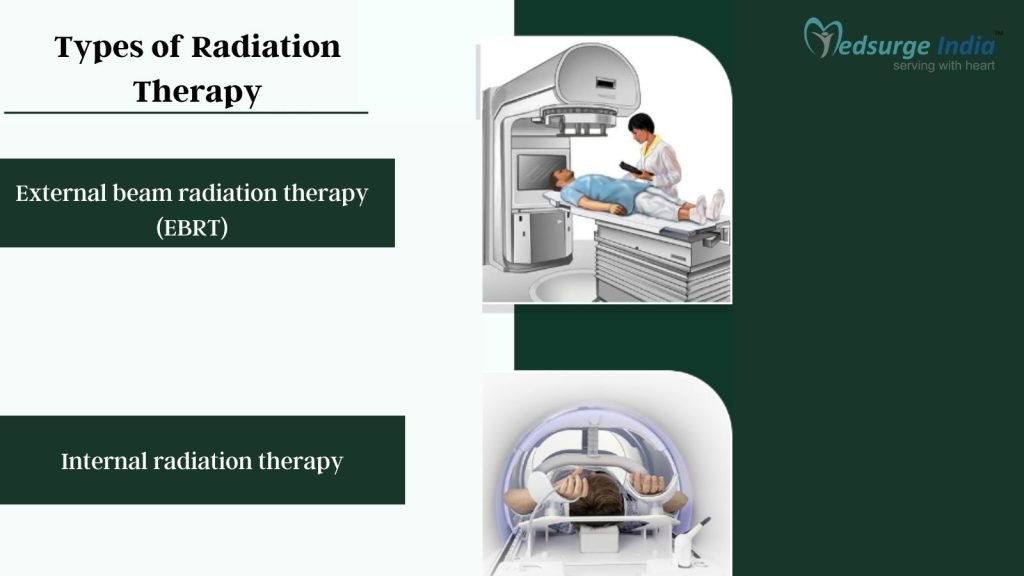
Types of Radiation Therapy
There are two major Types of Radiation Therapy in India
- External beam radiation therapy (EBRT)
- Internal radiation therapy
Both types function by damaging the DNA of a cancer cell. Cancer cells die and tumors shrink when their DNA instructions to grow and multiply are not present.
About External Beam Radiation Therapy
The most prevalent type of radiotherapy in India is external beam radiation therapy (EBRT). A machine directs high-energy radiation beams at the tumor during EBRT. X-rays, electrons, or protons are the most frequent kind of energy. Precision is essential in EBRT. Your radiation oncologist will create a treatment plan that will use radiation to target the tumor while avoiding healthy tissue.
There are many forms of EBERT Available in India:
- 3D Conformal Radiation Therapy: It uses CT scans and computer software to generate a 3D model of the tumor. The gadget guides radiation beams that target the cancer site while preserving healthy tissue, using the model as a guide.
- Intensity-modulated radiation treatment (IMRT): It is a type of radiation therapy that is more advanced. IMRT employs a number of radiation beams with varying dose intensities. It gives a larger dosage of radiation to the tumor while delivering lower doses to healthy tissue.
- Arc-based radiation is a type of IMRT: In which energy beams of changing intensity are directed in a rotational arc-like pattern. This approach provides radiation faster than regular IMRT. Volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) and tomotherapy are two types of arc-based radiation.
- Image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT): It is a type of EBRT in which the radiation machine acquires a low-dose X-ray or small CT scan prior to each treatment. This image aids in treatment site alignment, resulting in more precise radiation delivery.
- Particle therapy: It is a type of radiation therapy that uses protons rather than photons (X-rays). Protons can give the same radiation dose to the tumor while reducing radiation damage to healthy tissues in some persons.
- Stereotactic radiosurgery: Often known as Gamma Knife radiosurgery, employs high doses of concentrated radiation to surgically remove small brain tumors. Unlike surgery, it does not involve any cutting. This treatment typically takes one to five days.
- SBRT (stereotactic body radiation therapy): This treatment employs high doses of targeted radiation to eradicate tumors outside of your brain. It, like stereotactic radiosurgery, destroys tumors with surgical accuracy but without actual surgery.
- Intraoperative radiation therapy (IORT): This technique administers radiation during surgery. After a tumor has been physically removed, IORT removes any leftover cancer cells that aren’t safe to remove surgically.
About Internal Beam Radiation Therapy
Internal radiation therapy delivers radiation to cancer cells inside your body. It is used to treat minor tumors in the head, neck, breast, cervix, uterus, or prostate.
Internal radiation can be received from a solid or liquid source:
- Brachytherapy: It places a solid radioactive source, known as a “seed,” inside or next to a tumor. The source emits radiation into a narrow area, killing cancer cells. Some implants deliver low amounts over extended periods of time (weeks). Others may deliver high doses for shorter periods of time (in minutes). Some brachytherapy implants are only transitory. Others remain in your body indefinitely. They eventually stop emitting radiation.
- Systemic therapy: It involves the administration of liquid radioactive material into your bloodstream in order to detect and remove cancer cells. Some types are swallowed. Others will require an injection into a vein (IV). Radionuclide therapy (radioimmunotherapy) is one treatment option. A radioactive protein recognises certain cancer cells, attaches to them, and then releases radiation to kill them via radioimmunotherapy.
You can also learn more about the Radiation Therapy Cost in India here.
How Individuals are Prepared for Radiation Therapy in India?
- A physical exam and imaging may be required for internal radiation therapy. Your Radiation Oncologist in India will discuss how you can prepare for the procedure based on how the radiation will be delivered.
- External beam radiation therapy (EBRT) in India begins with a planning session known as a simulation. Simulation is a treatment planning stage that allows you to customize your treatment.
- Internal radiation therapy in India is often administered in a hospital or a designated outpatient treatment room. Your radiation oncologist may introduce the radiation implant using a catheter, which is a small flexible tube. You will be given anesthesia for this treatment so that you do not feel any pain or discomfort during the process. You will get radioactive fluid through an IV with the systemic kind of internal radiation therapy.
- With EBRT, you lie on a table in the same position as in simulation. The radiation machine moves around you but never touches you. A radiation therapist, a type of healthcare worker, controls the machine from a separate room. You can communicate with each other at any moment by using an intercom. As it moves, the equipment delivers precise doses of radiation to the tumor. During treatment, you will not feel anything.
- After getting Internal radiation therapy in India often allows you to go home the same day following a short recovery period. You may need to stay in the hospital on occasion while your body emits trace levels of radiation. Small amounts of radiation may be secreted through body fluids such as perspiration, pee, and blood during systemic (IV) radiation therapy.
- You should be able to carry on with your normal daily activities before and after the EBRT. There is no risk of radiation exposure to others.
Types of Cancer Treated with Radiation Therapy
External beam radiation is often used by doctors to treat the following forms of cancer:
- Breast cancer
- Lung cancer
- Prostate cancer
- Colon cancer
- Head and Neck Cancer
According to the best oncologists in India, brachytherapy may be a highly successful treatment for tumors in specific regions of the body, such as the:
- Cervix
- Vagina
- Uterus
- Rectum
- Head and neck
- Eye
When radiation therapy is used in combination with another treatment, such as surgery or chemotherapy called as adjuvant treatment.
Before surgery, some patients may receive radiation therapy to reduce a tumor and make it easier to remove. Other people might have it after surgery to kill cancer cells that the procedure missed.
Best Oncologists in India
Best Cancer Treatment Hospitals in India
- Fortis Hospital Gurgaon
- Fortis Hospital Noida
- Manipal Hospital Dwarka, Delhi
- HCG Cancer Centre, Bangalore
- Amrita Hospital, Faridabad
- Indraprastha Apollo Hospital New Delhi
Bottom Line
Radiation therapy alone may be sufficient to cure certain early-stage cancers. It is essential to understand that a human cannot be exposed to an infinite amount of radiation. As a result, doctors limit the therapy to one portion of the body and limit the overall quantity received by a person over their lifetime. Although radiation therapy does not usually cause pain, it might have undesirable side effects. If a person is in pain, they ought to inform their medical team.
Radiation therapy can have an impact on a person’s capacity to have children. Before beginning treatment, it is best to consult with a doctor about this possibility.



 (1).png)