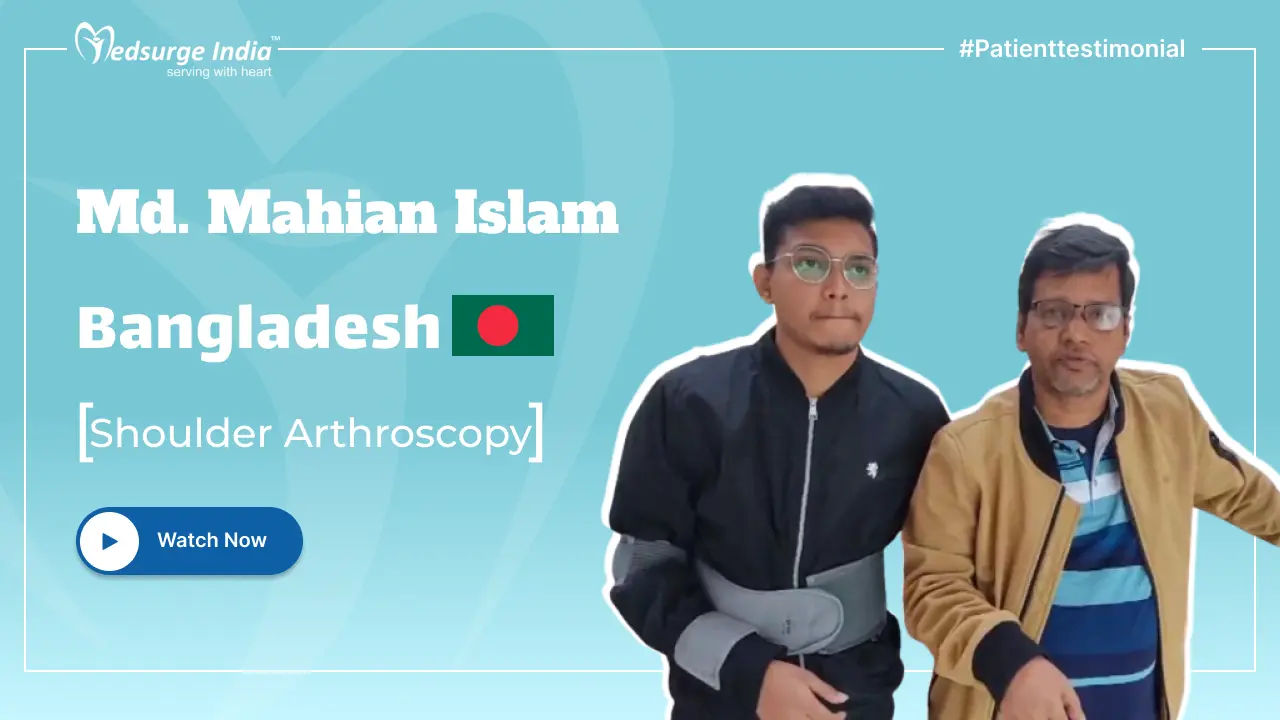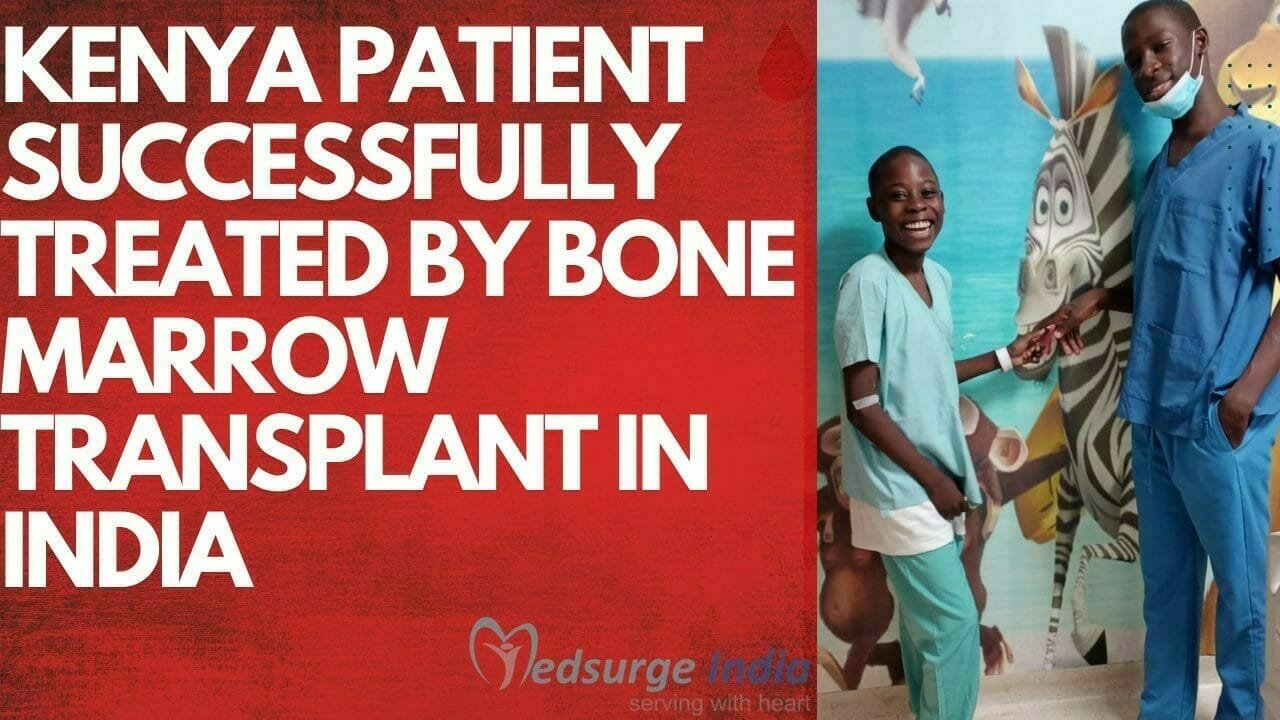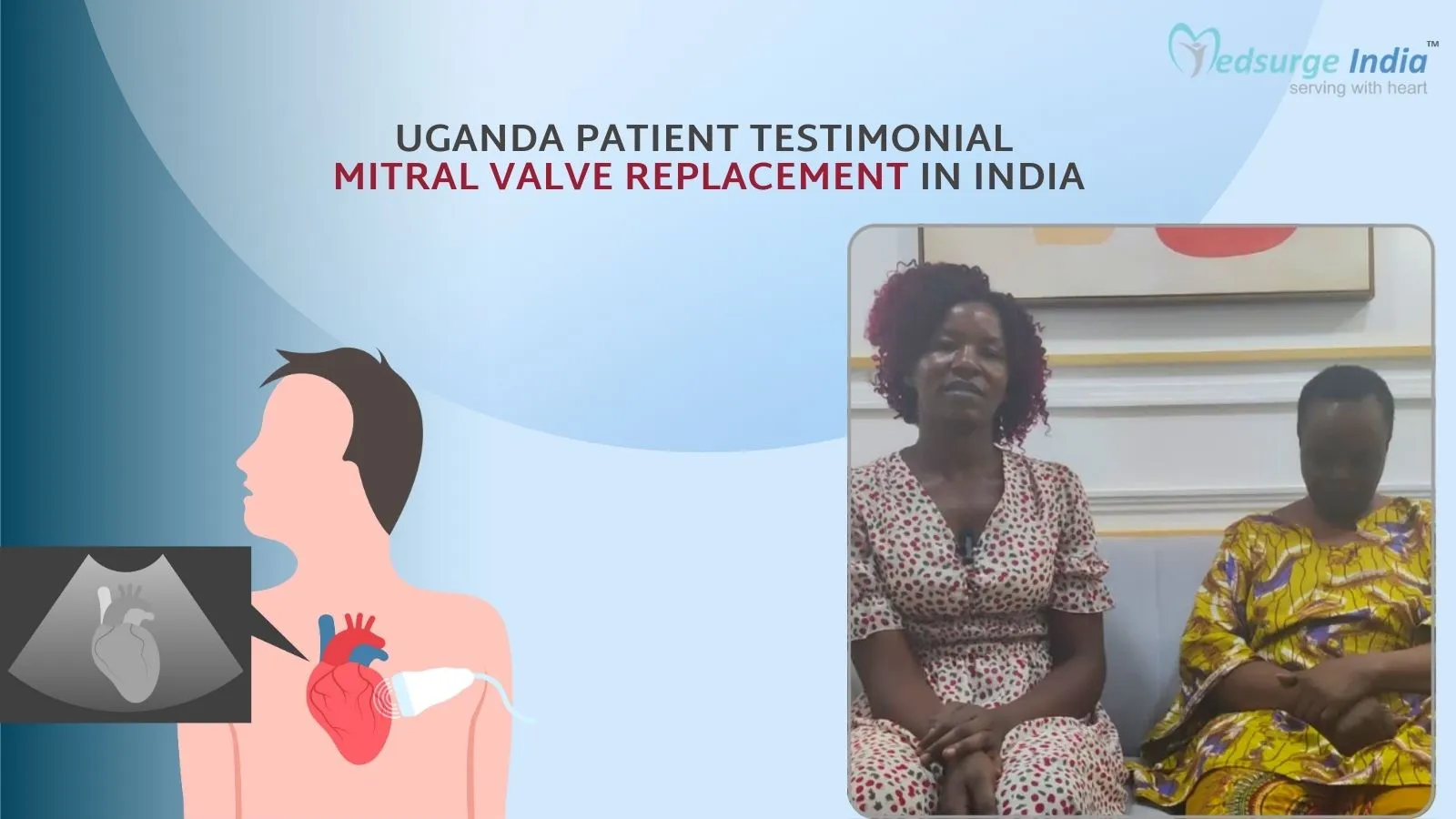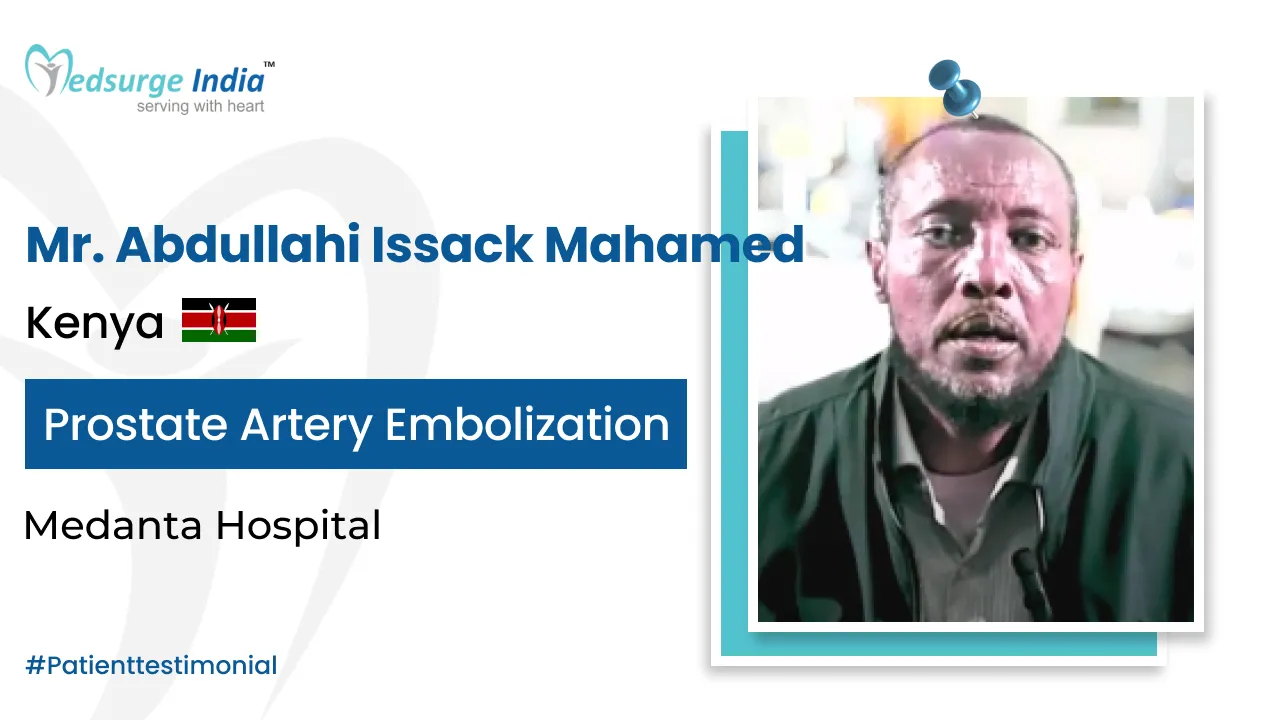
Myelofibrosis is a chronic and progressive kind of blood cancer known as a “myeloproliferative neoplasm”. It is characterized by abnormal development and the function of bone marrow cells that make blood cells, which results in the production of scar tissue in the marrow. When the bone marrow becomes damaged, it is unable to produce enough blood cells, resulting in anemia, spleen and liver enlargement, fatigue, and other issues. Myelofibrosis can also lead to acute myeloid leukemia in some cases.MF generally progresses slowly, and some people may go years without experiencing any symptoms. Others, on the other hand, may deteriorate over time and demand treatment. Patients must be monitored on a frequent basis in both circumstances. For most patients, the goal of myelofibrosis treatment in India is to alleviate symptoms, shrink an enlarged spleen, improve blood cell counts (i.e., anemia), and lower the risk of complications.
The myelofibrosis treatment cost in India depends upon the fees of highly qualified hematologists who specialised to focuses on treating blood-related disorders.
What Is Myelofibrosis?
Myelofibrosis is a rare kind of blood cancer in which fibrous scar tissue replaces the bone marrow (the soft, spongy substance inside most bones). It’s classified as a type of chronic leukemia. When myelofibrosis occurs on its own, it is called primary myelofibrosis. If it occurs as the result of a separate disease, it is known as secondary myelofibrosis (e.g. scar tissue in the bone marrow as a complication of autoimmune disease).
Immature blood-forming cells can develop into three types of specialized blood cells in the bone marrow: red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets. When a single cell’s DNA undergoes a change (mutation), the mutation is passed on to subsequent cells when the damaged cell divides.
As time passes, a number of aberrant cells are produced. They can also acquire new mutations over time, making cancer cells more aggressive. They may eventually be able to take the place of regular bone marrow cells. The ability of the bone marrow to create normal blood cells begins to deteriorate. Outside of the bone marrow, abnormal blood-forming cells can proliferate in the liver, lungs, lymph nodes, and other organs.
What Are the Symptoms of Myelofibrosis?
For many years, a person with myelofibrosis may have no symptoms. During the early phases of the disease, about one-third of patients show no symptoms. However, during the course of the disease, people may experience the following condition or symptoms of myelofibrosis:
- Breathing problems
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Feeling ache or fullness behind your ribcage on your left side
- Sweating during night
- Fever
- Bone ache
- Appetite loss and weight loss
- Bleeding gums or nosebleeds
- Enlarged liver and spleen
- Portal Hypertension
- Anemia
- Frequent Infection
What Are the Causes of Myelofibrosis?
Myelofibrosis develops when the DNA of bone marrow stem cells alters (mutates). The stem cells have the potential to reproduce and divide into many types of blood cells, such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
The cause of genetic alterations in bone marrow stem cells is unknown.
The mutations are passed on to new cells as the mutant blood stem cells reproduce and divide. As more of these altered cells are produced, the effects on blood production become more serious. The final outcome is frequently a deficiency in red blood cells, which causes the anemia characteristic of myelofibrosis, as well as an excess of white blood cells and varied levels of platelets. The typically spongy bone marrow gets scarred in persons with myelofibrosis.
In persons with myelofibrosis, several unique gene mutations have been discovered. The Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) gene mutation is the most prevalent. CALR and MPL are two less frequent mutations. Some individuals with myelofibrosis do not have any gene mutations that can be identified. Knowing if these gene mutations are linked to your myelofibrosis might help determine your prognosis and treatment options.
Primary myelofibrosis occurs when myelofibrosis develops on its own. Patients with other bone marrow cancers, such as essential thrombocythemia (excess platelets) or polycythemia vera, may develop myelofibrosis (production of excess red blood cells). Post-essential thrombocythemia or post-polycythemia vera myelofibrosis is the medical term for this condition.
Myelofibrosis Treatment Cost In India
On average, Myelofibrosis Treatment Cost in India starts from USD 2,800. The pricing of the treatment will depend on the type of place or the hospital you choose.
Types of Treatment Procedures for Treating Myelofibrosis Treatment in India
| Treatment | Starting Price |
| Splenectomy | USD 3,200 |
| Chemotherapy | USD 3,500 |
| Radiation Therapy | USD 3,200 |
| Targeted Therapy | USD 2,800 |
Estimated prices depending on different cities in India
| Cities | Starting Price |
| Delhi | USD 2,800 |
| Gurgaon | USD 2,800 |
| Noida | USD 2,800 |
| Mumbai | USD 2,900 |
| Hyderabad | USD 2,800 |
| Chennai | USD 2,800 |
| Kolkata | USD 2,800 |
| Bangalore | USD 2,900 |
Note: Do remember that the pricing and the treatment for Myelofibrosis Treatment cost in India will vary depending on the patient’s choice and other various factors.
Factors That Can Affect Myelofibrosis Treatment Cost in India
The following here are some variables that can affect Myelofibrosis Treatment Cost in India:
- Medication costs.
- Duration of treatment.
- Geographical location.
- Hospitalization expenses.
- Government policies and subsidies.
- Medical tourism packages.
- Hospital reputation and infrastructure.
- The expertise and experience of medical professionals.
- The type and frequency of diagnostic procedures.
- The choice of treatment modality.
Furthermore, even the standard and grade of medical care and amenities are comparable to those of the most prestigious healthcare facilities in the world, even when the expense of lodging, meals, and transportation is taken out. Also, under the direction of the most skilled physicians, Medsurge India provides patients with the lowest Myelofibrosis Treatment Cost in India.
How the Diagnosis of Myelofibrosis is done?
Your doctor will conduct a physical examination and inquire about your medical history, as well as any current symptoms. An enlarged spleen or anemia will be checked by the doctor.
There are a variety of diagnostic tests that can be conducted for the diagnosis of myelofibrosis, including:
- CBC: A complete blood count (CBC) that shows a higher number of white blood cells and platelets but a lower number of red blood cells than usual could indicate myelofibrosis.
- Blood Tests: Uric acid, bilirubin, and lactic dehydrogenase levels that are elevated may indicate the presence of myelofibrosis.
- Analysis of gene mutations: Certain mutations linked to myelofibrosis can be found in blood cells.
- Bone Marrow Biopsy: A sample of bone marrow may be extracted for examination under a microscope during the biopsy.
- Imaging tests: An ultrasound test, X-Rays, and MRI may be used to check for spleen enlargement.
Get Free Cost Estimation
Procedure
How Myelofibrosis is Treated?
For most individuals, the goal of treatment for myelofibrosis in India is to alleviate the signs and symptoms of the disease. A bone marrow transplant may provide a possibility for a cure for some patients, but this treatment is extremely difficult on the body and may not be a viable solution for many others.
Your doctor may use one or several formulas to analyze your condition in order to identify which myelofibrosis treatments are most likely to help you. To designate a risk group that indicates the severity of the disease, these formulae take into account several factors of your cancer and your overall health.
People with low-risk myelofibrosis may not need treatment right away, whereas those with high-risk myelofibrosis may need to consider severe treatments including bone marrow transplantation. Treatment for intermediate-risk myelofibrosis is mainly focused on symptom management.
If Myelofibrosis causes severe anemia, you may need the following treatment:
- Blood transfusions
- Androgen therapy
- Thalidomide and related medications
If an enlarged spleen is causing complications, your doctor may recommend different types of treatment. Your options may include:
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted drug therapy
- Splenectomy – surgical removal of the spleen
Bone Marrow Transplant
A bone marrow transplant, also known as a stem cell transplant, is a surgery that uses healthy blood stem cells to replace damaged bone marrow. The method for myelofibrosis uses stem cells from a donor (allogeneic stem cell transplant).
Although this treatment has the potential to cure myelofibrosis, it comes with a high risk of life-threatening adverse effects, including the possibility that the new stem cells would react against your body’s healthy tissues (graft-versus-host disease).
Many people with myelofibrosis do not eligible for this treatment because of age, disease stability, or other health issues.
Patients will receive chemotherapy or radiation therapy to destroy damaged bone marrow before a bone marrow transplant. Then you get stem cell infusions from a compatible donor.
Role of Drugs in Treatment
The goal for most patients is to manage the symptoms of myelofibrosis. Jakafi® (ruxolitinib) is the first medicine to receive FDA approval for the treatment of intermediate or high-risk myelofibrosis. It’s a Janus-associated kinase (JAK) signaling inhibitor that operates by inhibiting several kinases.
The medicine is taken orally. It helps to alleviate some of the symptoms of the disease, such as spleen enlargement, night sweats, itching, weight loss, and fever.
Suggestion
While MF may not always create symptoms in its early stages, it can later lead to major consequences, such as cancers that are more aggressive. Consult your doctor to identify the best treatment option for you and how to manage your symptoms.
Myelofibrosis is incurable, however allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) could be a cure. The treatment entails the patient’s immune system being replaced with that of a qualified donor. This new immune system searches for and kills malignant cells in the myelofibrosis patient’s bone marrow while still supplying healthy blood-forming bone marrow cells. The patient must undergo chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy prior to the transplant to weaken his or her own immune system so that the cells from the donor can survive.
The Most Important Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is Myelofibrosis a Cancerous Condition?
A: Myelofibrosis is a rare type of bone marrow cancer that interferes with your body’s natural blood cell manufacturing. Myelofibrosis is a disease that produces substantial scarring in the bone marrow, resulting in severe anemia that causes weakness and fatigue.
Q: Is It Possible to Recover from Myelofibrosis?
A: The only cure is a procedure known as allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Your stem cells don’t work properly in myelofibrosis. As a result of this scar tissue forms in your bone marrow.
Q: What Causes Death in Myelofibrosis?
A: Infections, bleeding, heart failure, post-splenectomy mortality, and transition into acute leukemia are the most prevalent reasons for death in people with primary myelofibrosis. Within the first ten years, leukemic transformation occurs in about 20% of patients with primary myelofibrosis.
Q: Is Myelofibrosis a Brain Disease?
A: Myelofibrosis can affect any part of the body, and tumors can form in places like the lymph nodes, spinal cord, and lungs. These tumors harm the brain because they cannot be removed from the body.
Q: Is Myelofibrosis Contagious?
A: These defective genes duplicate themselves. The harmful versions travel throughout your body and produce cells in your marrow that cause inflammation.
Top Hospitals for Myelofibrosis Treatment in India
Top Doctors for Oncology and Oncosurgery
Dr. Subhash Chandra Chanana
Senior Consultant
Experience: 51 years of experience
Marengo Asia Hospitals Formerly W Pratiksha Hospital, Gurgaon
Gurgaon, India
Dr Ajit Pai
Senior Consultant
Experience: 17 years of experience
Apollo Cancer Hospital, Chennai
Chennai, India
Dr Suchanda Goswami
Consultant
Experience: 15 years of experience
AMRI Hospital, Kolkata (Dhakuria)
Kolkata, India
Dr. Vaibhava Srivastava
Consultant
Experience: 9 years of experience
Apollo Medics Super Speciality Hospital, Lucknow
Lucknow, India
Dr. Bhavnaben Parikh
Experience: 19+ years of experience
Narayana Multispeciality Hospital, Rakhial, Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad, India
Dr. Sundaram Pillai
Consultant
Experience: 12 years of experience
Reliance Hospital, Navi Mumbai
Mumbai, India
Dr. Parmod Kumar
Experience: 15+ years of experience
Max Super Speciality Hospital Dehradun
Dehradun, India
Dr. Gunjan Baijal
Experience: 20+ years of experience
Manipal Hospital, Panaji, North Goa
North Goa, India