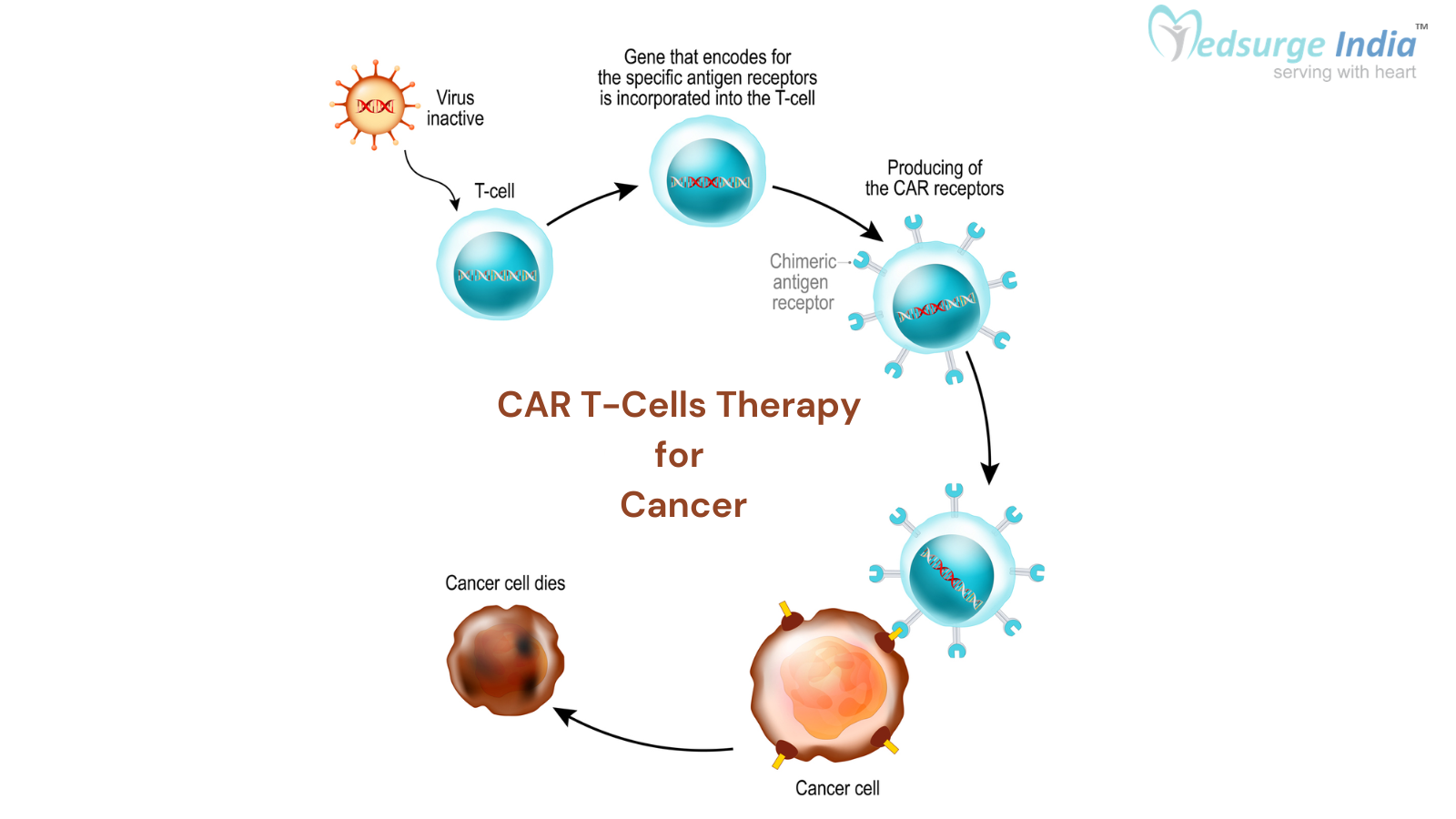
How Does CAR T-Cell Therapy Work in Treating Cancer
A form of immunotherapy known as “chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy” alters the immune system of a cancer patient to make it more adept at locating and eliminating cancer cells. The immune system of a human is extremely intricate and encompasses numerous distinct cell types and bodily systems. A lymphocyte is one of these cells; it is a type of white blood cell that fights infection. There are numerous varieties of lymphocytes, and one of them is known as a T-cell. T cells are used in CAR T-cell therapy because they often eliminate malignant cells and virus-infected cells.
Cancer cells are known to evade the immune system’s regular defenses, but thanks to CAR T-cell treatment, some cancer cells can now be more easily found and eliminated by T cells.
What is CAR T-Cell Therapy?
T-cells are effective at warding off infections. However, it can be challenging for them to distinguish between a cancer cell and a normal cell. In order to avoid detection, the cancer cells might conceal themselves.
Researchers are looking for strategies to train T-cells to recognize cancer cells. CAR T-cell therapy is one method that could be used to achieve this.
How does CAR T-Cell Therapy Work?
For this kind of therapy, a cancer patient must first be sent to a specialized facility. Then, a collection of their T-cells is required. It is important to understand that prior cancer treatments frequently have an impact on T-cells and may leave them less healthy. When T-cells are transformed into CAR T- cells, they should ideally be in the best condition. This frequently implies that a person’s T-cells must be collected during a break in therapy. This means that in order to collect as many healthy T-cells as possible, the doctor needs take special care to ensure that cancer won’t be overly active or result in too many symptoms while therapy is delayed.
The T-cells are gathered via a procedure known as “Apheresis”, once a predetermined length of time has passed without treatment. During apheresis, the patient’s blood is cycled through a device that removes T-cells before returning the remaining blood to them. After that, a manufacturer receives the cells and turns them into CAR T-cells, which normally takes 3 to 6 weeks. The person’s regular T-cells are activated, proliferated, and infected with a virus during the manufacturing process, which leads to genetic change and the addition of the CAR to the T cell. The CAR T-cells are then transported back to the cancer patient’s doctor frozen.
Before injecting the CAR T-cells into the cancer patient, the doctor administers a brief course of chemotherapy termed lymphodepletion over the course of two to three days. This prevents the body’s immune system from misinterpreting the CAR T-cells as aberrant and rejecting them. The CAR T-cells are then removed from the freezer, defrosted, and administered through the blood in a manner akin to a blood transfusion.
At this point, the CAR T-cells begin to function. They move about the body looking for cancer cells, activating, growing, utilizing cytokines to recruit support, and then eradicating cancer.
How is CAR T-Cell Treatment Carried Out?
CAR T-cell treatment directs T cells to target an antigen, which is present on the surface of particular cancer cells and is perceived as dangerous by the body. To aid the T cells in achieving this focus, a protein is added to their surface during the creation of CAR T cells. The chimeric antigen receptor, or CAR, is the name of this protein. The CAR protein is really composed of the following 3 proteins: Two proteins that tell the T cell to activate when the first protein binds to an antigen on the cancer cell and one protein that identifies antigens on the cancer cell. A T cell is referred to as a “CAR T cell” when a CAR has been introduced to it. CAR T cells search for cells that carry the antigen encoded into the CAR protein, such as specific cancer cells, as they float around the body.
A CAR T cell becomes activated when it comes into touch with an antigen in a cancer cell. CAR T cells that have been activated proliferate and alert other immune system components to travel to the cancer cell’s location. Cytokines are the name given to these signaling proteins. Following considerable inflammation concentrated on the cancer cell brought on by all of these cytokines and activated T cells, the cancer cell eventually perishes. Cancer may go into remission, which indicates that it has either temporarily or permanently disappeared if all of the cancer cells are eliminated.
What Common Adverse Effects Might CAR T-Cell Therapy Cause?
- Cytokine release syndrome (CRS), also known as excessive immune activation, can be exceedingly damaging to a cancer patient. After receiving CAR T cells, CRS usually starts within a few days to two weeks and ends between days to weeks.
- People getting CAR T-cell treatment experience CRS in a variety of ways. Others require intensive care unit (ICU) level treatment, which may entail using equipment to help keep the patient alive. Some people just have a high-grade fever, some have low blood pressure and/or low oxygen levels, and still, others require this level of care. Being hospitalized in the ICU following CAR T-cell therapy is less frequent now that medical professionals are considerably more adept at controlling CRS.
- Cytokines can sometimes harm the brain during CAR T-cell therapy, generating a condition known as immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS). Other symptoms of ICANS include shaking, mild to severe disorientation, and, less frequently, seizures. Additionally, memory loss may result. ICANS almost often co-occurs with CRS and typically manifests 1 to 4 weeks after CAR T-cell injection, after CRS. Though some symptoms may take longer to go away, ICANS is reversible.
- It’s crucial to remember that CAR T cells kill every cell they are directed at, even healthy cells. Typically, this causes an immune system that is compromised for several months after therapy. This could result in uncommon infection forms that are often seen in persons with severe immunodeficiencies.
- During this phase of recovery, a patient undergoing CAR T-cell therapy should exercise extra caution and let their doctor know if they experience any symptoms, such as a fever.
The adverse effects of this novel medication may not yet be fully understood by medical professionals. known negative effects consist of:
- allergic response
- the syndrome of cytokine release
- alterations in the brain (neurological side effects)
- greater potential for infection
- excessive levels of uric acid in the blood brought on by the breakdown of cancer cells
- quickly (tumor lysis) (tumor lysis)
Which Forms of Cancer Have CAR T-Cell Treatment Been Shown Effective Against so Far?
CAR T-cell therapy approvals are evolving quickly. Here are some diseases that have shown effective against the treatment such as:
- Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL)
- Follicular lymphoma
- Mantle cell lymphoma
- Multiple myeloma
- B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
Pediatric and young adult patients up to age 25 are the cancer types that are currently treated with CAR T-cell therapy. Five CAR T-cell medications were authorized by the American Food and Drug Administration as of March 2021. (FDA). Depending on the indication, all of these approvals are for patients whose cancer has returned after undergoing at least one prior form of therapy due to the substantial adverse effects associated with CRS and ICANS.
There is a tonne of further research being conducted on CAR T-cell therapy, such as looking at how to make CAR T-cell therapy safer for patients and how to use currently FDA-approved medicines for new purposes or in patients who haven’t had as much treatment. Many people in the medical field are optimistic about the future of CAR T-cell therapy and what it can imply for cancer patients as long as research into the treatment is conducted.
Authorized CAR T-Cell Therapy
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has given the green light for CAR T-cell treatments to treat certain leukemias, lymphomas, and multiple myeloma cases. After alternative forms of treatment have been exhausted, CAR T-cell therapy is frequently used.
Current approved CAR T-cell therapy examples include:
- Idecabtagene vicleucel, also known as ide-cel (Abecma)
- Ciltacabtegene autoleucel, also known as cilta-cel (Carvykti)
- Tisagenlecleucel, also known as tisa-cel (Kymriah)
- Axicabtagene ciloleucel, also known as axi-cel (Yescarta)
- Brexucabtagene autoleucel, also known as brexu-cel (Tecartus)
- Lisocabtagene maraleucel, also known as liso-cel (Breyanzi)
In order to treat other types of cancer, numerous additional CAR T-cell therapies (and related types of therapy) are currently being investigated in clinical studies.
How can Medsurge India Help
Medsurge India is a prestigious support system for patients looking for doctors, hospitals, and specialized treatments. We’ll find the most suitable medical options for you. Regarding your medical issues, our team will give you a list of certified, reputable, and trusted doctors and hospitals. Additionally, we offer a treatment strategy that fits your budget. Apart, we assist patients with obtaining travel authorizations, medical visas, and a multitude of other things.
Reference
- https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/research/car-t-cells
- https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/types/immunotherapy/t-cell-transfer-therapy