Bone Marrow Transplant – Types, Procedures & Risks
The spongy liquid substance in the middle of some bones is called bone marrow. It contains a large number of stem cells, and its primary function is to produce blood cells that circulate throughout the body. The pelvis (hip) bones have the most marrow and consist of a high number of stem cells. As a result, cells from the pelvic bone are frequently employed in bone marrow transplants. To extract a large number of healthy stem cells, enough marrow must be removed.
Bone Marrow Transplant
A bone marrow transplant is a surgical process that replaces bone marrow that has been injured or destroyed by disease, infection, or chemotherapy. During this treatment, blood stem cells are transplanted into the bone marrow, where they create new blood cells and accelerate the growth of new marrow.
The spongy, fatty tissue inside your bones is called “Bone Marrow”. It is responsible for the formation of the following blood components:
- Red blood cells are oxygenated and nutrient-carrying cells that circulate throughout the body.
- Infection-fighting agents, white blood cells
- The platelets are responsible for clotting
In addition to these blood-forming stem cells, bone marrow contains immature blood-forming stem cells called hematopoietic stem cells. These cells have already differentiated and can only replicate themselves. In spite of this, these stem cells are unspecialized, which means they can divide through cell division and either remain as stem cells or differentiate and mature into a variety of blood types. Your bone marrow contains stem cells that make new blood cells throughout your lifetime.
Your damaged stem cells are replaced with healthy cells in a bone marrow transplant. This promotes your body to stimulate the production of adequate white blood cells, platelets, or red blood cells to prevent infections, bleeding disorders, and anemia.
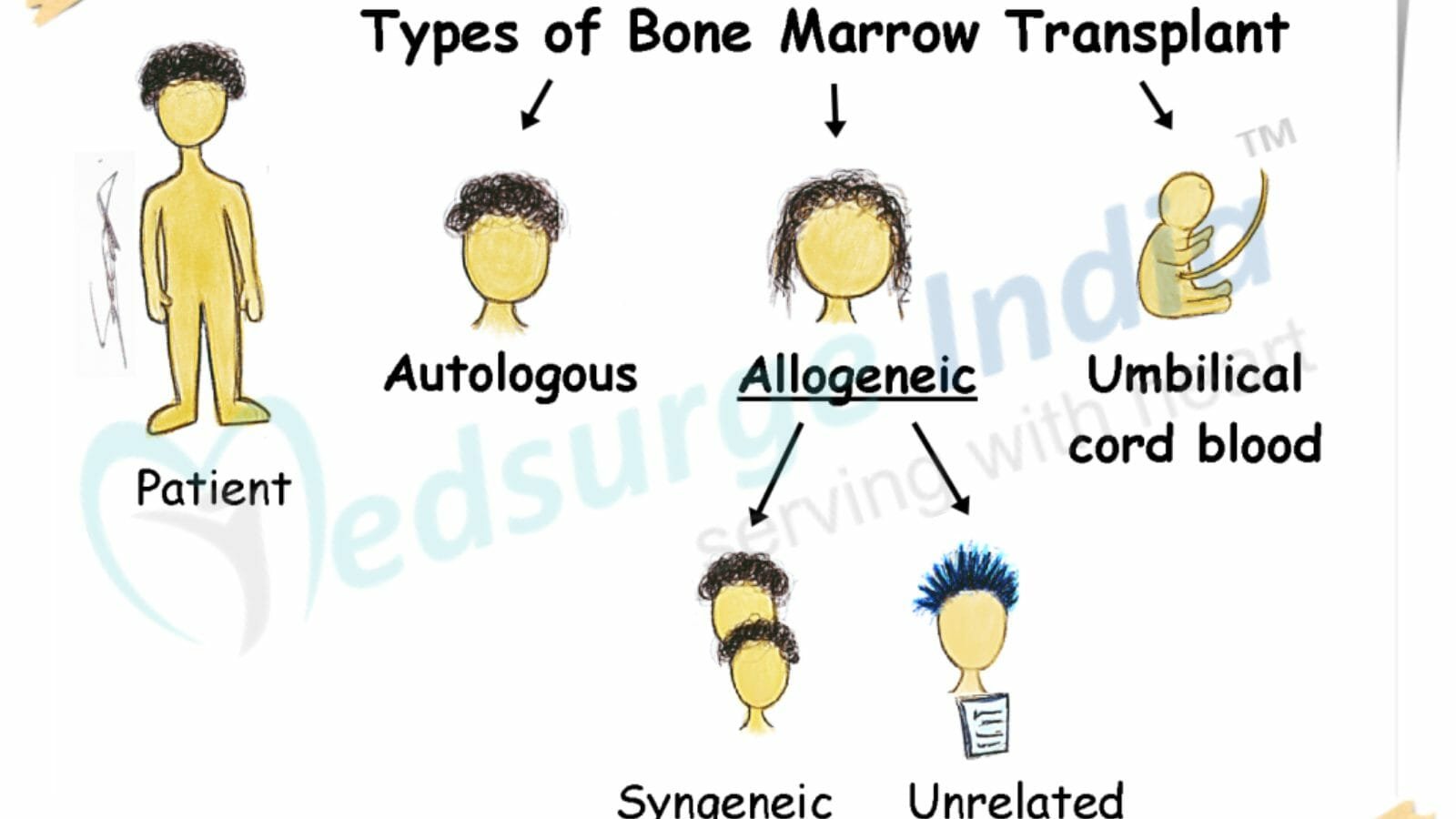
Types of Bone Marrow Transplants
When the bone marrow is destroyed by disease, chemotherapy, or radiation, stem cell transplants are performed to regenerate the stem cells. The bone marrow transplant procedure is known by many names depending on where the stem cells come from:
- Bone Marrow Transplant (BMT)
- Cord Blood Transplant
- Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplant
To attempt to destroy all the cancer cells in a normal stem cell transplant for cancer, very high doses of chemo are employed, sometimes in combination with radiation therapy. The stem cells in the bone marrow are also killed by this treatment. This treatment can be termed Myeloablation or Myeloablative Therapy. Stem cells are delivered (transplanted) shortly after treatment to replace those that were killed. Similar to a blood transfusion, the replacement stem cells are injected into a vein. The objective would be for the transplanted cells to settle in the bone marrow, develop, and produce healthy blood cells over time.
Recommended Video: Bone Marrow Transplant – Types, Procedures & Risks
This procedure is termed Engraftment. Bone Marrow Transplants are into two major broad categories:
Autologous: The term “auto” refers to self. Autologous transplants involve stem cells from the same person receiving the transplant, effectively making the patient their own donor.
The removal or harvesting of your own stem cells is the initial stage in this type of transplant. Your stem cells are extracted from your bone marrow or blood and preserved.
The stem cells are thawed and reintroduced into you after you have received heavy doses of chemo and/or radiation as part of your myeloablative therapy.
Certain leukemias, lymphomas, and multiple myeloma are treated with this type of transplant. Other tumors, such as testicular cancer and neuroblastoma, as well as certain cancers in children, are quite often treated with this kind of transplant. Other disorders that can also be treated with autologous transplants include systemic sclerosis, multiple sclerosis (MS), and systemic lupus erythematosus (lupus).
Allogenic: Allo is a Latin word that signifies “other.” Allogeneic transplants use stem cells from someone other than the patient, either a familiar or non-familiar donor.
Allogeneic stem cell transplantation uses donor stem cells. The stem cells in the most common type of allogeneic transplant come from a donor whose tissue type is quite similar to yours. A close relative, generally a brother or sister, is the best donor. If you don’t have a suitable match in your family, a national registry may help you find a donor from the general population.
Allogeneic transplants function similarly to autologous transplants. The donor’s stem cells are taken and preserved or frozen. The donor’s stem cells are thawed and administered to you after you have high doses of chemo and/or radiation as your myeloablative therapy.
Allogeneic transplantation is commonly used to treat sickle cell anemia, leukemia, lymphomas, myelodysplastic syndrome, and other genetic blood disorder such as Aplastic Anemia, Fanconi anemia, Thalassemia, Pancytopenia.
Procedure
- Several tests will be performed prior to your transplant to determine what type of bone marrow cells you require.
- Before getting new stem cells, you may need to have radiation or chemotherapy to destroy all cancer cells or marrow cells.
- Transplanting bone marrow can take up to a week. As a result, you must make preparations prior to your first transplant session.
- Your immune system will be reduced throughout therapy, affecting your ability to fight infections. As a result, you’ll be admitted to a specialized division of the hospital dedicated to those undergoing bone marrow transplants. As a result, you are less likely to come into contact with anyone who can infect you.
Helpful – All You Need to Know About Pancytopenia
How it is Performed?
For being curious, it is similar to getting a blood transfusion. Bone Marrow Transplantation is purely a blood transformation process, no organ will be taken out or removed surgically.
Bone marrow cells from your donor will be extracted a day or two before your procedure if you are undergoing an allogeneic transplant. Your own cells will be acquired from the stem cell bank if they are needed.
There are two methods for collecting cells.
A needle is used to collect cells from both hipbones during a bone marrow harvest. You will be sleepy and pain-free during this treatment since you will be sedated.
What to Expect After Transplantation?
The genetic compatibility of the donor and recipient is critical to the effectiveness of a bone marrow transplant. Finding a good match among unrelated donors can be extremely challenging at times.
Your engraftment will be checked on a regular basis. It usually takes between 10 and 28 days to complete following the initial transplant. An increasing white blood cell count is the first indicator of engraftment. This indicates that the transplant is producing new blood cells.
A bone marrow transplant usually requires three months of recovery time. However, full recovery might take up to a year. Many factors play a role in recovery, including:
- The disorder being treated
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation
- A match of donors
- Where the transplant will be performed
Risks & Side-Effects of Transplantation
Many of the concerns can arise quickly after the transplantation from the bone marrow being wiped out by drugs or radiation just before the procedure. Others might be unexpected side effects of the conditioning procedure includes following:
- Ulcer or Mouth Sores
- Vomiting and Nausea
- Trouble in Eating Habits
- Hair Loss
- Infection
- Breathing Problems or Lung Disorders
The new cells will grow into red and white blood cells, as well as platelets, once they reach your marrow. This procedure, known as engraftment, can take up to 3 to 4 weeks.
Final Evaluation
You will first be analyzed to check if you are suitable for a transplant. A transplant is extremely exhausting on the body. Transplants can be life-saving for many people, but for others, difficulties can lead to serious complications or even death. Before you begin, you should evaluate the advantages and disadvantages.
Before undergoing a transplant, you should consult with your doctors about the procedure and its potential side effects. It is also beneficial to speak with individuals who have received transplants.
You may also be interested in – About Sickle Cell Anemia | Sickle Cell Treatment | MIOT Hospital Chennai