Cancer Treatment in India
Unlock Exclusive Discount : Your Gateway to Premium Healthcare with Medsurge India Health Value Card.

Unlock Exclusive Discount : Your Gateway to Premium Healthcare with Medsurge India Health Value Card.


Cancer is a condition in which some cells in the body grow out of control and spread to other parts of the body.
Cancer can begin practically anywhere in the trillions of cells that make up the human body. Human cells normally expand and multiply (via a process known as cell division) to generate new cells as needed by the body. Cells die as they become old or injured, and new cells replace them.
This ordered process can sometimes break down, resulting in aberrant or damaged cells growing and multiplying when they shouldn’t. Tumors, which are masses of tissue, can grow from these cells. Tumors may or may not be malignant (benign).
Cancerous tumors can infect adjacent tissues and spread to other parts of the body, resulting in the formation of new tumors (a process called metastasis). Malignant tumors are another name for cancerous tumors. Many malignancies, including leukemias, create solid tumors, whereas cancers of the blood do not.
Benign tumors do not penetrate or spread into neighboring tissues. Benign tumors rarely reappear after being excised, although malignant tumors do. However, benign tumors can grow to be extremely enormous. Some, such as benign brain tumors, can produce serious symptoms or even be fatal.
Proto-oncogenes, tumor suppressor genes, and DNA repair genes are all affected by the genetic alterations that contribute to cancer. These changes are commonly referred to as cancer’s “drivers.”
Proto-oncogenes play a role in normal cell division and proliferation. These genes can become cancer-causing genes (or oncogenes) if they are mutated in specific ways or are more active than usual, allowing cells to grow and survive when they should not.
Tumor suppressor genes are also engaged in cell division and growth control. Certain mutations in tumor suppressor genes can cause cells to divide uncontrollably.
DNA repair genes are responsible for repairing damaged DNA. Cells with mutations in these genes are more likely to generate mutations in other genes and chromosome alterations, such as chromosome duplications and deletions. These alterations may lead the cells to become malignant if they occur together.
There are over 100 different types of cancer. Cancers are frequently called after the organs or tissues in which they develop. Lung cancer, for example, begins in the lungs, while brain cancer begins in the brain. Cancers can also be classified based on the type of cell that caused them, such as epithelial or squamous cells.
Cancers that start in specific types of cells fall into the following categories:
Other types of tumors are the following:
Cancer Treatment cost in India pricings may change due to the following reasons. Here are the variables that can affect Cancer Treatment Cost in India:
In addition, the quality and level of medical care and facilities offered are on par with renowned healthcare institutions worldwide, even after factoring in the costs of accommodation, meals, and transportation. Moreover, under the guidance of highly proficient doctors, Medsurge India ensures that patients receive the most affordable Cancer Treatment Cost in India.
The type of cancer, its stage, whether cancer has spread, and your overall health all influence treatment options. The goal of treatment is to eliminate as many malignant cells as possible while minimizing damage to neighboring healthy cells. This is made feasible by technological advancements.
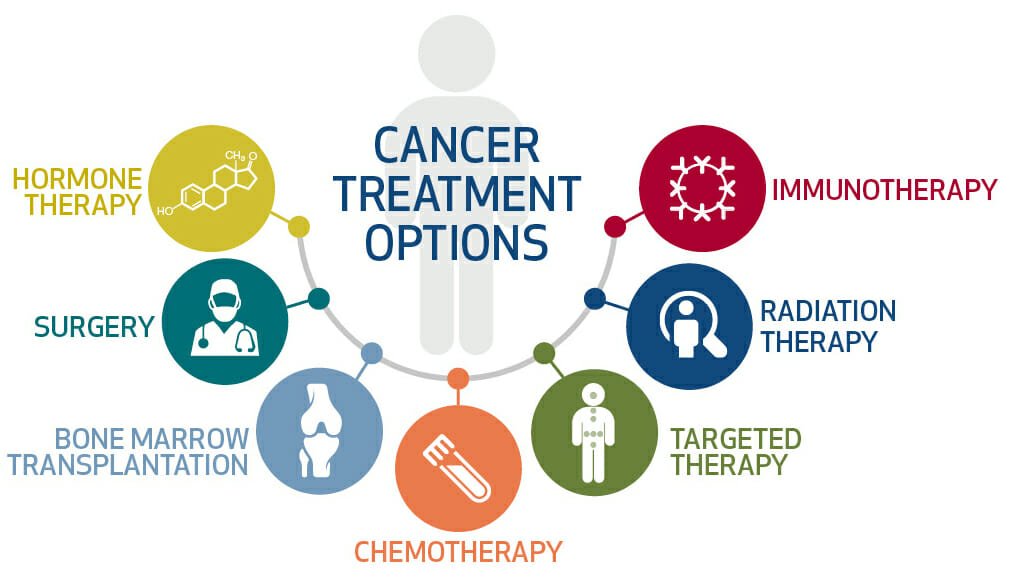
The major treatments for cancer are as follows:
A bone marrow transplant allows your doctor to treat your cancer with larger chemotherapy doses. It can also be used to replace bone marrow that has become diseased.
Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy, often known as biological therapy, is a cancer treatment that makes use of your body's immune system. Because your immune system does not detect cancer as an intruder, it can thrive unchecked in your body. Immunotherapy can assist your immune system in "seeing" and attacking cancer.
Hormone Therapy: Some cancers are driven by hormones in the body. Breast cancer and prostate cancer are two examples. Cancer cells may stop developing if such hormones are removed from the body or their effects are blocked.
Targeted Drug Therapy: Targeted medication therapy focuses on cancer cells' unique defects that allow them to survive.
Cryoablation: Cold kills cancer cells with this treatment. A thin, wand-like needle (cryoprobe) is introduced through your skin and directly into the malignant tumor during cryoablation. To freeze the tissue, a gas is fed into the cryoprobe. The tissue is then allowed to defrost. To kill cancer cells, the freezing and thawing process is performed numerous times during the same therapy session.
Radiofrequency Ablation: This treatment heats cancer cells, causing them to die, utilizing electrical energy. During radiofrequency ablation, a doctor inserts a small needle into the cancer tissue through the skin or an incision. High-frequency radiation goes through the needle and heats the surrounding tissue, killing the cells in the area.
The same cancer type in one person can be significantly different from the same cancer type in another. Researchers are uncovering subgroups within a single form of cancer, such as breast cancer, that each requires a particular therapeutic method.
Active measures to reduce cancer risk are classified as cancer prevention. The great majority of cancer cases are caused by variables in the environment. Many of these environmental influences are under our control as a result of our lifestyle decisions. As a result, cancer can usually be avoided. Between 70% and 90% of common malignancies are caused by environmental factors, making them potentially avoidable.
Tobacco, excess weight/obesity, poor food, physical inactivity, alcohol, sexually transmitted infections, and air pollution are all risk factors that might be avoided to save more than 30% of cancer fatalities. Poverty may also be regarded as an indirect risk factor for human malignancies. Some environmental factors, such as naturally occurring background radiation and cancers caused by hereditary genetic abnormalities, are not controllable and so cannot be prevented through personal action.
Factors to be considered as precautions are the following:
Palliative care is a type of treatment that aims to make the patient feel better while also attempting to treat cancer. Palliative care entails taking steps to alleviate physical, emotional, spiritual, and psychosocial suffering. Unlike treatments that try to destroy cancer cells directly, palliative care's primary purpose is to improve quality of life.
A: Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells within a part of the body that might spread to other areas of the human body.
A: Cancer not only causes bodily life-threatening illness status but also contributes to the psychological and fiscal crisis in a patient’s lifestyle.
A: This was the situation sooner but today with all the healthcare progress the prognosis and life expectancy is great.
A: Metastasis implies that cancer (tumor cells) has spread into other parts of human anatomy and invading there, the outcomes of metastasis might be severe life-threatening.
A: Some are added to every letter to indicate the size or extent of the principal tumor and the degree of cancer spread (higher number indicates a larger tumor or more disperse).
A: 40 percent of cancer Brought on by tobacco or pan masala particularly the oral and lung cancer.
A: Anyone can create cancer; however, the danger of getting it increases with age.
Certain cancers could be connected to a few occupational dangers.
A: Oncologist is specialized doctors for the treatment of cancer, maybe a surgical oncologist, radiation oncologist, or medical oncologist.
A: Any persistent bulge or swelling
A: About two-thirds of that cancer is associated with lifestyle and can be averted
A: Following the individual presents with symptoms that are imagining, a Battery of tests and analyses are performed to confirm the diagnosis of malignancy
A: This helps in specifying the Degree to Which the cancer cells Have spread in human anatomy
When the diagnosis of cancer has been confirmed the doctor will Do additional staging tests and based on the outcomes and overall health and age of the individual, the treatment strategy is devised that may necessitate surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, or a combination of them.
A: The goal of the treatment is to kill as many cancerous cells and minimize the damage to normal cells.
A: The major treatment for cancer would be:
A: Yes some therapy modalities can cause Infertility, so you might consider your alternatives for maintaining your eggs or sperm for future usage.
A: Chemotherapy is a treatment system that utilizes powerful chemicals to destroy fast-growing cells inside the body.
A: Chemotherapy may be Applied as the main remedy for cancer.
After other remedies, to kill concealed cancer cells
Treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiation, are potential.
A: Chemotherapy drugs may be given in various ways, such as:
A: Tests to test for heart health to find out whether it is safe to start chemotherapy.
Fixing existing illnesses, to Decrease the risk of complications as chemotherapy can decrease the body’s ability to resist infections, it is important to see a physician to rule out disease concentration in the mouth.
A: If you can work through therapy depends upon:

Surgical Oncologist
Senior Consultant
12+ Years
BLK Max Super Speciality Hospital, New Delhi
View Doctor
Medical Oncologist
Associate Consultant
10+ years
Meitra Hospital, Calicut, Kerala
View Doctor
Radiation Oncologist
Senior Consultant
10+ years
Apollo Proton Cancer Centre, Chennai
View Doctor
Surgical Oncologist
Senior Consultant
8+ years
Meitra Hospital, Calicut, Kerala
View Doctor

Medical Oncologist
Consultant
15+ years
Care Hospitals HITEC City
View Doctor
Surgical Oncologist
Sr. Consultant & Associate Clinical Director
20+ years
Care Hospitals HITEC City
View Doctor
Surgical Oncologist
Senior Consultant
13+ years
Care Hospitals HITEC City
View Doctor
Surgical Oncologist
Senior Consultant & Head of the Department
22+ years
Care Hospitals HITEC City
View Doctor
Surgical Oncologist
Senior Director
15+ years
Fortis Hospital, Vasant Kunj, Delhi
View Doctor









By using our site, you agree to our Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy and Refund Policy. Medsurge India provides reliable healthcare information and treatment options to support informed decision-making. Our content is designed to support and complement the guidance of your treating doctor, helping you feel informed and confident throughout your healthcare journey. We also Accept International Payments.

Copyright © 2025 NSM ONLINE SOLUTIONS PRIVATE LIMITED. All rights reserved.