Q: What Is the Difference Between Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, and Hepatitis C?
A: Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, and Hepatitis C are due to three distinct viruses. Even though their symptoms are similar and every one of them strikes the liver, their modes of transmission are somewhat distinct. Each of the three starts as severe illnesses but Hepatitis A doesn’t become chronic and enhances without medication. On the flip side, Hepatitis B and C can become persistent if toxin proceeds to stay in the bloodstream for over six months. A chronic disease may result in serious complications such as cirrhosis or cancer. Vaccines are available for Hepatitis A and B, but not for Hepatitis C.
Q: Who Is at Risk of Contracting HCV?
A: Following type of people are at risk of contracting Hepatitis C-
- People who use injectable drugs
- People with HIV
- People receiving kidney dialysis for long
- Children of an infected mother
- People born between 1945 and 1965
- People who have got piercings or tattoos
- Healthcare workers who handle blood
- Patients with diseases that require blood from donors
Q: Can Hepatitis C Be Prevented?
A: Hepatitis C could be avoided by taking precautions just. Although vaccines for hepatitis A and B can be found, there’s not any vaccine available to shield against hepatitis C. Since the principal source of transmission of HCV is infected blood, the illness can be prevented from spreading by preventing the contact with contaminated blood, e.g. consumption of needles, private things such as razor and nail clipper ought to be prevented.
Q: Can Hepatitis C Be Cured?
A: Yes, hepatitis C is also curable. The therapy therapies and medications have proven a success rate of 95 percent in removing HCV. Medicines for distinct genotypes are readily available. To get genotypes 1, 2, and 3, the direct-acting antifungal medications (DDA) can be found and for genotypes 4, 5, and 6, elderly kinds of medications are there which have a fantastic reply but take more time to take care of the disease.
Q: What Is the Contagious Period for Hepatitis C?
A: There’s not any particular period of time of contagiousness of Hepatitis C. Since the disease is spread via the exposure to contaminated blood, the blood of an infected individual remains infectious until the HCV is totally removed from his entire body.
Q: If I Had Hepatitis C in the Past, Can I Get Re-infected?
A: Yes, Someone treated from hepatitis C isn’t immune from accessing the HCV disease again. Hepatitis C is very likely to recur in HIV infected individuals. But, Re-infection could be prevented by appropriate care and refraining in risky tasks like sharing needles and individual products.
Q: What Are Genotypes of HCV?
A: Hepatitis C virus can be classified on the basis of genes that are similar. This categorization is referred to as genotype. There are just six HCV genotypes labeled from 1 to 6 weeks. These have subtypes tagged with letters of an alphabet. It’s necessary to understand more about the genotype when diagnosing the HCV as distinct HCV genotypes are treated with various medicines. Although an individual has been infected by a single genotype, however, it’s also possible that someone might get infected by more than 1 genotype, concurrently.
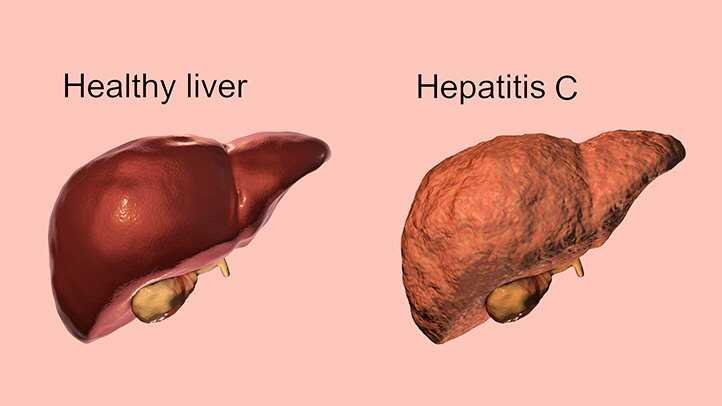
Q: What Complications Are Associated With Hepatitis C?
A: Many people with chronic hepatitis C don’t develop complications. But patients with chronic hepatitis B are at risk of getting liver cirrhosis or liver cancer. Some folks might require a liver transplant. Individuals with alcoholic and obesity are at greater risk of suffering from complications of hepatitis C.
Q: Will I Need a Liver Transplant If Infected With HCV?
A: Though hepatitis C is treatable and curable, but sometimes it transforms to liver cirrhosis or liver cancer, leading to adrenal liver disease and liver failure. In these situations, the only possible remedy is a liver transplant.
Q: What Care Should Be Taken by People With Chronic Hepatitis C?
A: Standard monitoring of those sufferers of chronic Hepatitis Cby experienced physician is needed. Alcohol has to be rigorously avoided to prevent additional liver damage. Any other drugs, nutritional supplements, and over-the-counter medication shouldn’t be taken without consulting the physician. In the event of chronic hepatitis C, then the individual ought to take the vaccinations of Hepatitis A and B.
Q: How Should Infected Blood Spills Be Cleaned from Surfaces to Ensure That HCV Is Removed?
A: All blood flow, such as the dried blood, should be washed and the surface ought to be disinfected with bleach and water. Gloves should be used while cleansing the blood spills.
Q: What Are the Side Effects of Hepatitis C Drugs?
A: The side effects of hepatitis C drugs depend on the medicines used. The common side effects are:
- Fatigue
- Loss of hair
- Headache
- Anemia
- Depression and nervousness
- Confusion
Q: How Much Does it Cost to Treat HCV?
A: The newest drugs DAA to deal with HCV are extremely powerful. There are various medications for various genotypes. Many times a combination of medications is required to heal HCV. The expense of these medications is extremely high and an individual with average income finds it hard to manage it. The expenses of therapy operate in many thousands of US dollars. But, you can find generic medications available in a number of countries that cost just a couple hundred US dollars for the comprehensive treatment.















 (1).png)