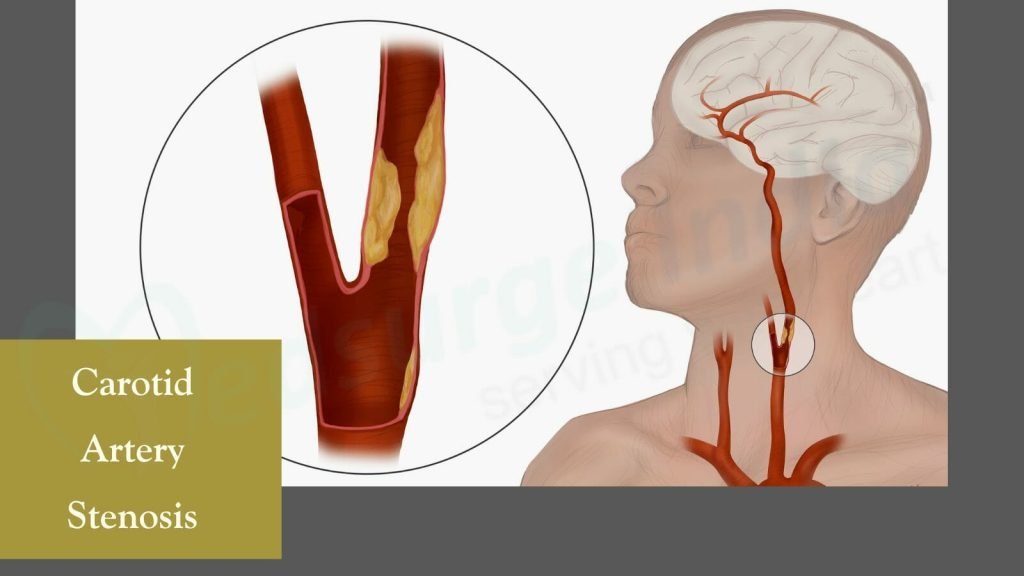
A treatment to treat carotid artery stenosis is carotid artery stenosis surgery. Endarterectomy is a surgical operation that can be used for the treatment of carotid artery stenosis.
The carotid artery is responsible for supplying blood to your brain and face. Each side of your neck has one of these arteries. Plaque, a fatty substance, can partially or completely restrict blood flow in this artery. This can cut off blood flow to your brain, resulting in a stroke.
The goal of carotid artery stenosis treatment is to improve blood flow to the brain. There are two ways for treating a plaque-clogged carotid artery.
What Is Carotid Artery Stenosis?
Carotid artery stenosis is a disorder in which the main artery on either side of your neck, the carotid artery, becomes clogged. Plaque is the material that causes the blockage (fatty cholesterol deposits). You are more likely to have a stroke if plaque stops the regular flow of blood through your carotid artery. Atherosclerosis is the accumulation of plaque.
There are two carotid arteries in your neck, one on each side. These are the main arteries that supply blood to the brain, face, and head. These arteries are smooth and open when they are healthy, like a clean pipe that permits fluid to flow freely without obstruction. The circulatory system of your body is a network of tubes that transport blood (which contains nutrients and oxygen) to all parts of your body.
Carotid artery stenosis can affect one or both of the two arteries in your neck. Without medical attention, this disease can deteriorate over time, leading to a stroke with serious complications, including death.
What Are the Symptoms of Carotid Artery Disease?
A stroke can result from carotid artery stenosis symptoms. Pieces of plaque (or platelets that form on plaque) migrate to your brain in the type of stroke that frequently results from carotid stenosis. Ischemic stroke is a type of stroke that occurs when the blood supply to a part of the brain is cut off. Your brain cells or neurons begin to die when this obstruction is permanent.
A transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a type of “mini-stroke” that occurs when plaque and/or platelets temporarily block a tiny brain artery. A TIA is common before an ischemic stroke in many persons. In order to avoid cell death, it’s critical to get therapy for these conditions as soon as feasible.
A TIA or stroke can cause the following symptoms:
- One-half of your face is drooping.
- Speech that is slurred or has difficulty forming words and interacting with others.
- Loss of vision in one eye is accompanied by the sensation of a black shade falling across your field of vision.
- One-half of your body is losing sensation.
- Muscle weakness and loss of strength on one side of the body.
You may not notice any symptoms if you have carotid artery stenosis that hasn’t caused a stroke.
What Are the Causes of Carotid Artery Stenosis?
When fatty material called plaque builds up inside the arteries, it causes carotid artery disease. The plaque buildup is referred to as artery hardening (atherosclerosis).
The plaque can constrict or block the carotid artery over time. It could also cause a clot to form unexpectedly. A stroke can occur when a clot fully stops an artery.
The following are some of the risk factors for artery blockage or narrowing:
- Tobacco use (people who smoke one pack a day double their risk for stroke)
- Diabetes
- Blood pressure that is too high
- Cholesterol and triglyceride levels are high.
- Getting older
- Stroke history in the family
- Use of alcoholic beverages
- Use of recreational drugs
- Trauma to the neck that could result in a tear in the carotid artery
How is Carotid Artery Stenosis Diagnosed?
Frequent diagnosis of Carotid artery stenosis is done after a stroke has occurred. The symptoms motivate your doctor to perform a comprehensive examination for any type of blockage, which may lead to the diagnosis of carotid artery stenosis. During a stethoscope exam of your neck, your provider may hear an irregular sound termed a bruit (whistling sound) or murmur, which can be used to identify this condition. Several tests are used by doctors to establish a diagnosis of carotid artery stenosis and determine the extent and location of the obstruction. These tests may involve the following:
- Ultrasound
- Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA)
- Cerebral Angiography
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Your healthcare professional will check to see if you have the problem, how large it is, and where it is located throughout the diagnosis procedure. Mild, moderate, and severe carotid artery stenosis are the three types of stenosis. A minor blockage is defined as one that is less than 50% blocked. This suggests that your artery is only partially obstructed. A moderate blockage is defined as a blockage that is between 50% and 79%. The most serious classification is when the majority of your artery is blocked, which can range from 80% to 99%.
Carotid Artery Stenosis Treatment Cost in India
Carotid Artery Stenosis Treatment Cost in India starts from Rs 2 Lakh (2400 USD), the treatment price will also vary depending on the overall diagnosis of the patient’s conditions. Carotid Artery Stenosis Treatment Cost in India offers some of the best contemporary hospitals and technology, and it’s also inexpensive when compared to Western countries.
Carotid Artery Stenosis Treatment Cost in Different Cities in India:
| Cities | Starting Price |
| Delhi | Rs 2 Lakh (2400 USD) |
| Gurgaon | Rs 2,03,000 (2450 USD) |
| Noida | Rs 1,82,000 (2200 USD) |
| Mumbai | Rs 2,07,500 (2500 USD) |
| Hyderabad | Rs 1,82,000 (2200 USD) |
| Chennai | Rs 2,00,000 (2400 USD) |
| Kolkata | Rs 1,90,900 (2300 USD) |
| Bangalore | Rs 2,07,500 (2500 USD) |
Note: Please be aware that the costs listed above are only an indication of what the treatment will cost initially and may change depending on a number of variables.
Factors That Can Affect Carotid Artery Stenosis Treatment Cost in India
The standard and excellence of medical treatment and amenities are comparable to those of the most prominent healthcare facilities in the world, even after deducting the cost of lodging, meals, and transportation. Following here are some variables that can affect Carotid Artery Stenosis Treatment Cost in India:
- Medication costs.
- Duration of treatment.
- Geographical location.
- Hospitalization expenses.
- Government policies and subsidies.
- Medical tourism packages.
- Hospital reputation and infrastructure.
- The expertise and experience of medical professionals.
- The type and frequency of diagnostic procedures.
- The choice of treatment modality.
The most affordable Carotid Artery Stenosis Treatment Cost in India is offered to patients worldwide by Medsurge India, under the supervision of highly qualified medical professionals.
Get Free Cost Estimation
Procedure
Carotid Artery Stenosis Treatment in India
The major goal of carotid artery stenosis treatment in India is to slow or stop the condition from progressing. This begins with lifestyle changes such as a nutritious diet, exercise, and quitting smoking. A daily infant dose of aspirin, as well as blood pressure and cholesterol-lowering medicines, may be administered.
Your provider may use a surgical technique called carotid artery stenosis surgery or endarterectomy to remove plaque from the carotid artery through an incision in more severe cases or cases generating symptoms of TIA or stroke. Alternatively, your surgeon may insert a stent into the blocked artery using a big needle hole. This will widen the artery to its correct size while trapping the plaque between the stent and the wall, blocking blood flow. Each person who needs therapy for the carotid disease is evaluated by a vascular surgeon or expert to determine which of these procedures is appropriate for them.
To delay the progression of atherosclerosis, lifestyle changes and some drugs may be indicated if the blockage is minor to moderate:
- Lifestyle Changes: Quitting smoking, losing weight, changing your diet to include more healthy foods, lowering your salt intake, and exercising consistently are all recommended lifestyle improvements.
- Medication to control blood pressure or lower cholesterol: A daily aspirin or other blood-thinning drugs may be recommended by your doctor to avoid blood clots if you have high blood pressure or high cholesterol.
Surgical treatment may be recommended if the blockage is severe:
Carotid endarterectomy: In severe situations of stenosis, carotid endarterectomy is often required. While the patient is under general anesthesia, a surgeon makes an incision to remove plaque and any damaged portions of the artery.
Angioplasty and stenting of the carotid artery: A less intrusive alternative for severe stenosis. A catheter is threaded from an incision in the groyne to the obstruction site during this surgery. They inflate a balloon tip to open the artery once they arrive. A stent may be inserted into the artery to enlarge it and keep it open.
Conclusion
Carotid artery stenosis becomes more likely as you become older. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is the most important thing you can do to avoid this condition and its complications, such as a stroke. A healthy lifestyle includes things like exercising, eating nutritious foods, and not smoking. Make follow-up meetings with your primary care physician and vascular specialist on a regular basis. Consult your doctor about strategies to keep your heart and circulatory system in good shape.
The Most Important Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What Percentage of Blockage in Carotid Stenosis Requires Surgery?
A: For symptomatic individuals with a 70% to 99% blockage in the carotid artery, surgery is the best option. It can, however, be considered for patients with a blockage of 50% to 69 percent. For individuals with moderate to severe carotid stenosis, doctors concur that surgery is the most effective treatment choice.
Q: How Fast Does Carotid Stenosis Progress?
A: The average rate of stenosis advancement over two years is not significant, although it is higher in diabetic patients with baseline stenosis larger than 50% who continue to smoke. Serial DUS rescreening should be limited to high-grade stenosis, with follow-up performed every 1-2 years.
Q: What Is Life Expectancy After Carotid Artery Surgery?
A: The average time spent following up was 2.6 years (range 1-7 years). The observed 5-year survival rate was 85.2%, compared to a normal population’s predicted rate of 92%.
Q: How Serious Is a Blocked Artery in the Neck?
A: Patients with carotid stenosis often have minor cognitive issues that do not interfere with daily activities. The mild cognitive deterioration induced by carotid artery stenosis, on the other hand, may develop into dementia later in life.
Q: How Serious Is a Blocked Artery in the Neck?
A: Fatty deposits (plaques) obstruct the blood vessels that supply blood to your brain and head, causing carotid artery disease (carotid arteries). The obstruction raises your chances of having a stroke, which occurs when the blood supply to the brain is cut off or severely diminished.
Top Hospitals for Carotid Artery Stenosis Treatment in India
Top Doctors for Cardiology And Cardiac Surgery
Dr. Abhishek Parmar
Senior Consultant
Experience: 18+ years of experience
Narayana Multispeciality Hospital, Rakhial, Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad, India
Dr. Sanjay Mittal
Director
Experience: 27 years of experience
Medanta – The Medicity, Gurgaon
Gurgaon, India
Dr. Anand Lingan
Senior Consultant
Experience: 12+ years of experience
Narayana Multispeciality Hospital, R S Naidu Nagar, Mysore
Mysore, India
Dr. Murali Babu
Experience: 33+ years of experience
SS Narayana Heart Centre, Davangere
Davangere, India
Dr. Sumanta Chatterjee
Consultant
Experience: 11 years of experience
AMRI Hospital, Kolkata (Dhakuria)
Kolkata, India
Dr. Chiran Babu A
Senior Consultant
Experience: 23 years of experience
Kauvery Hospitals, Electronic City, Bangalore
Bangalore, India
Dr. P V Rao
Senior Consultant
Experience: 35 years of experience
Apollo Hospitals, Greams Road, Chennai
Chennai, India
Dr. Rajesh T R
Senior Consultant
Experience: 26 years of experience
Kauvery Hospitals, Electronic City, Bangalore
Bangalore, India
Dr. K Kannan
Consultant
Experience: 23 years of experience
Prashanth Multi Speciality Hospital Chennai
Chennai, India
Dr. Niranjan K Reddy
Experience: 21+ years of experience
RL Jalappa Narayana Heart Centre, Tamaka, Kolar
Kolar, India