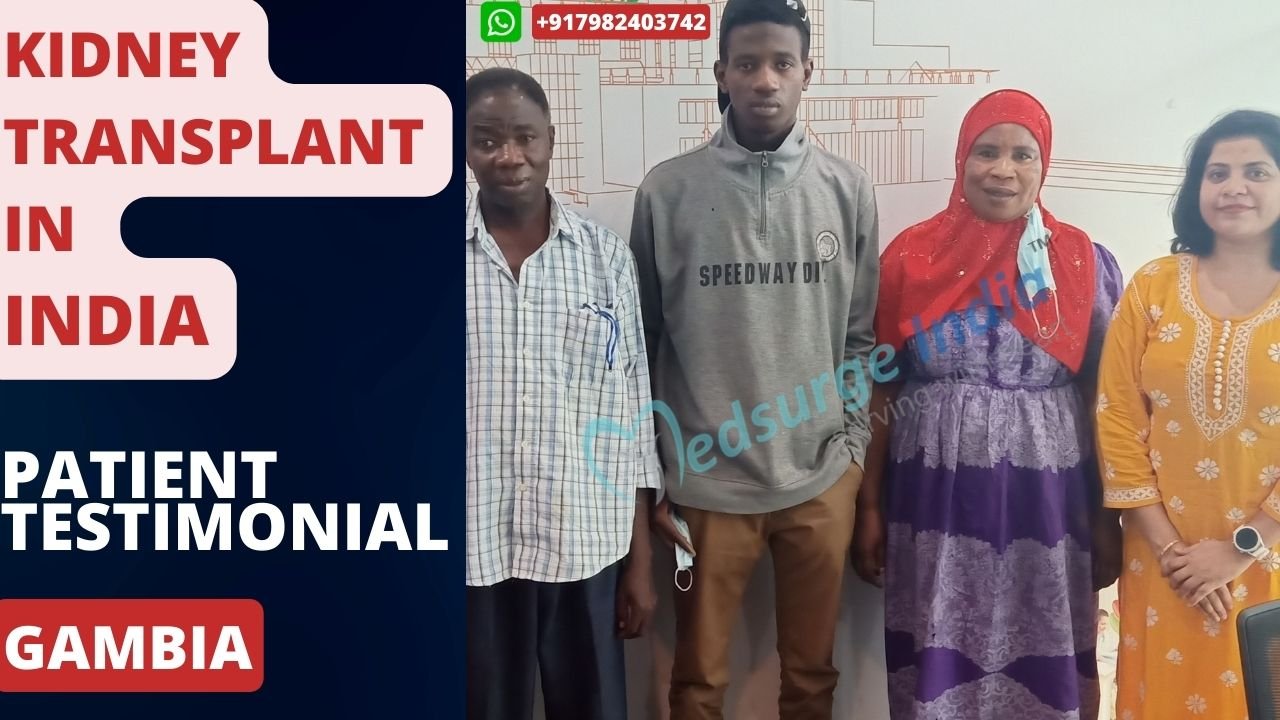
This is a group of rare cancers characterized by aberrant cell proliferation within a woman’s uterus. These begin in cells that would typically form the placenta during pregnancy. Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Treatment in India differs depending on the type of disease. Surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy are usually used in conjunction.
The Gestational trophoblastic disease treatment cost in India is totally dependent upon the type of hospital selected by the patient for the treatment as well as the stage at which the tumor has progressed.
What Is Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD)?
Choriocarcinoma is a form of gestational trophoblastic disease that occurs in the uterus of a woman. It is a collection of tumors that develop in a woman’s uterus. A tumor is an abnormal cell development in any portion of the body that may or may not contain cancer cells (malignant) or (benign). A GTD usually starts in the layer of trophoblast cells that surrounds an embryo (tropho means nutrition and blast indicates bud or early development). The placenta, the organ that shelters and nourishes the growing fetus, develops from this layer of trophoblast cells. The tumor can be malignant or non-cancerous and arises from the placenta in GTD. Therefore, Choriocarcinoma is a malignant variant of gestational trophoblastic disease.
GTD stands for gestational trophoblastic disease and refers to a variety of conditions:
- Hydatidiformes Moles (HM)
- Complete HM
- Partial HM
Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia (GTN):
- Choriocarcinomas
- Invasive Moles
- Placental-site trophoblastic tumors (PSTT; very rare)
- Epithelioid trophoblastic tumors (ETT; even more rare)
What Are the Symptoms of Gestational Trophoblastic Disease?
GTD symptoms can be similar to those of a normal pregnancy. They could resemble a spontaneous abortion, often known as a miscarriage, or an ectopic pregnancy. However, the following signs and symptoms of gestational Trophoblastic condition may indicate a problem:
- Bleeding from Vagina
- Vomiting
- Abdominal swelling
- Anemia
- Hyperthyroidism
- Pre-eclampsia
- Cysts developed in the ovary
- Undefined weight loss
- Pelvic Pain or Pressure
- Toxic Pregnancy
Symptoms might appear weeks, months, or even years after a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
If a malignant GTD has migrated beyond the uterus at the time of diagnosis, further symptoms may appear depending on where the disease is located. In this situation, GTD could be misinterpreted as another medical problem.
For example, choriocarcinoma spreading to the brain might cause bleeding that can be misdiagnosed as a brain aneurysm. A blood test for human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) can help the healthcare team better understand the condition.
What Are the Causes of Gestational Trophoblastic Disease?
Choriocarcinoma is rare cancer that develops as a result of an abnormal pregnancy. In this type of pregnancy, the baby may or may not develop.
Cancer can even develop after a healthy pregnancy. However, it is more common in full hydatidiform moles. At the start of a pregnancy, this is a growth that occurs inside the womb. Even after removal, the abnormal tissue from the mole can continue to grow and become malignant. About one-half of all women with choriocarcinoma had a hydatidiform mole or molar pregnancy.
Choriocarcinomas can also develop after an early failed pregnancy (miscarriage). They can also happen due to a genital tumor or an ectopic pregnancy.
The causes of GTD have a variety of reasons. Several risk factors linked to a woman’s pregnancy may raise her risk. They include:
- Age
- History of Molar Pregnancy
- History of Miscarriage
- Blood Type
- Birth Control Pills
The only way to avoid GTD is to avoid pregnancy. When making such family planning decisions, keep in mind that GTD is a rare occurrence. Prior abortion is not linked to the development of GTD. People who have had a molar pregnancy in the past or who are concerned about GTD for any reason should discuss their future risks with their doctors.
Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Treatment Cost in India
On average, Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Treatment Cost in India starts from USD 2500. The cost of the treatment will depend on the type of treatment you choose.
Types of Treatment Procedures for Treating Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Treatment in India
| Treatment | Starting Price |
| Surgery | USD 3100 |
| Chemotherapy | USD 800 |
| Radiation Therapy | USD 2800 |
| Targeted Therapy | USD 1100 |
Estimated prices depending on different cities in India
| Cities | Starting Price |
| Delhi | USD 2500 |
| Gurgaon | USD 2500 |
| Noida | USD 2500 |
| Mumbai | USD 2500 |
| Hyderabad | USD 2500 |
| Chennai | USD 2500 |
| Kolkata | USD 2500 |
| Bangalore | USD 2500 |
Note: Do remember that the pricing and the treatment for Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Treatment cost in India will vary depending on the patient’s choice and other various factors.
Factors That Can Affect Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Treatment Cost in India
The following here are some variables that can affect Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Treatment Cost in India:
- Medication costs.
- Duration of treatment.
- Geographical location.
- Hospitalization expenses.
- Government policies and subsidies.
- Medical tourism packages.
- Hospital reputation and infrastructure.
- The expertise and experience of medical professionals.
- The type and frequency of diagnostic procedures.
- The choice of treatment modality.
Furthermore, even the standard and grade of medical care and amenities are comparable to those of the most prestigious healthcare facilities in the world, even when the expense of lodging, meals, and transportation is taken out. Also, under the direction of the most skilled physicians, Medsurge India provides patients with the lowest Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Treatment Cost in India.
How Is the Diagnosis of Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Done?
A biopsy is the only sure technique for a doctor to determine whether a tumor is cancerous in most cases. A biopsy is when a doctor extracts a small sample of tissue for laboratory testing. If a biopsy is not possible, the doctor may recommend further tests to aid in the diagnosis of GTD.
When choosing a diagnostic test, your doctor may consider the following factors:
- The type of disease suspected
- Your signs and symptoms
- Your age and general health
- The results of earlier medical tests
The following tests, in addition to a physical examination, may be performed to diagnose GTD:
- Pelvic Examination
- Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) Test
- Ultrasound
- X-Rays
- CT or CAT Scan
- MRI
You should see a doctor who is either an oncologist or a gynecologist to get a correct diagnosis of GTD. Patients are frequently followed by a multidisciplinary team that includes an oncologist, a gynecologist, physiotherapists, and psychologists. Your treatment will be determined by your GTD stage.
Get Free Cost Estimation
Procedure
How Gestational Trophoblastic Disease is Treated?
GTD is usually curable, especially if detected early. Surgery and/or chemotherapy are the most common treatments for Gestational Trophoblastic Disease. The most frequent types of GTD therapies are listed below. Treatment for symptoms and side effects may be part of your treatment plan, which is an important element of medical care.
The type, stage, and risk category of GTD, as well as the patient’s preferences and overall health, all influence treatment options and recommendations. Three types of standard treatments are used by doctors are following:
Surgery: During an operation, the tumor and some surrounding healthy tissue are removed. It is frequently the primary and, in some cases, the only treatment for a molar pregnancy. The operation is usually performed by a gynecologist or gynecologic oncologist who specializes in eliminating tumors through surgery. The extent of surgery for GTD is determined by the tumor’s stage. Surgical procedures include:
- Suction dilation & curettage (D&C)
- Hysterectomy
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is a type of systemic therapy that is used to treat GTD. Chemotherapy is the use of medications to kill tumor cells by preventing them from growing, dividing, and producing new ones. Chemotherapy is usually highly effective in the treatment of molar pregnancy and certain types of gestational trophoblastic neoplasia (GTN). Chemotherapy is sometimes used alone, and other times it is used in combination with surgery.
Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy is a cancer treatment that involves the use of high-energy x-rays or other forms of radiation to kill or stop cancer cells from developing. Radiation therapy is divided into two types:
- External radiation therapy
- Internal radiation therapy
The type of gestational trophoblastic disease being treated determines how radiation therapy is administered. The treatment for the trophoblastic disease is external radiation therapy.
Suggestion
The medications used to treat GTD are under constant review. The best approach to understand the prescriptions given for you, their purpose, and any potential adverse effects or combinations with other medications is to speak with your doctor. It’s also crucial to inform your doctor if you’re taking any additional medications or supplements, whether prescription or over-the-counter. Herbs, vitamins, and other pharmaceuticals can interact with tumor-treating medications, resulting in terrible side effects or decreased efficacy.
The Most Important Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is GTD a Form of Cancer?
A: The majority of GTD is benign (non-cancerous) and does not spread, but some forms can turn malignant (cancerous) and spread to surrounding tissues or distant sections of the body.
Q: Is Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Curable?
A: Treatment for gestational trophoblastic disease and recurring disease GTD is a treatable condition. Women with hydatidiform moles have a good prognosis and rarely require treatment, but women with GTN have a good prognosis but must be treated.
Q: Is It Possible to Get Pregnant with GTD?
A: Following GTD treatment, you may be concerned about future pregnancies. Although there is a higher risk of recurring GTD, most women who have previously been treated for GTD have normal pregnancies. All subsequent pregnancies in women who have had GTD must be closely monitored.
Q: What Is the Duration of Chemo for Molar Pregnancy?
A: Six months after molar pregnancies, women with high but declining human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) concentrations can be treated with chemotherapy.
Q: Is It Possible to Have a Baby After a Molar Pregnancy?
A: Yes, you have a good possibility of becoming pregnant and having a healthy child again. The chances of another molar pregnancy are slim (about 1 in 80). It’s advisable not to try to conceive again until you’ve completed all of your follow-up treatment. This will take roughly 6 months for most ladies.
Top Hospitals for Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Treatment in India
Top Doctors for Oncology and Oncosurgery
Dr. Rishik Raj Pathak
Experience: 8+ years of experience
Narayana Superspeciality Hospital, Amingaon, Guwahati
Guwahati, India
Dr. Ritesh Pruthy
Principal Consultant
Experience: 16 years of experience
Max Superspecialty Hospital, Mohali
Mohali, India
Dr. Raghuram C. P
Consultant
Experience: 25 years of experience
Rainbow Children's Hospital & BirthRight by Rainbow, Bangalore
Bangalore, India
Dr. Vivek Agarwala
Senior Consultant
Experience: 17+ years of experience
Narayana Superspeciality Hospital, Shibpur, Howrah
Howrah, India
Dr. Amit Rauthan
Consultant
Experience: 20 years of experience
Manipal Hospital (Old Airport Road) Bangalore
Bangalore, India
Dr. Chandragouda Dodagoudar
Consultant , MBBS, MD, DNB
Experience: 22 years of experience
BLK Super Speciality Hospital, New Delhi
New Delhi, India
Dr. Durgatosh Pandey
Head of Department
Experience: 18 years of experience
Manipal Hospitals Dwarka, Delhi
New Delhi, India
Dr. Ramesh Sarin
Senior Consultant , MBBS, MS, FRCS, Fellowship
Experience: 40 years of experience
Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, New Delhi
New Delhi, India
Dr. Vijay Haribhakti
Consultant
Experience: 31 years of experience
Sir HN Reliance Foundation Hospital
Mumbai, India
Dr. S K Bala
Consultant
Experience: 10 years of experience
HCG EKO Cancer Centre, Kolkata
Kolkata, India
Dr. Moni Abraham Kuriakose
Visiting Consultant
Experience: 17 years of experience
Narayana Multispeciality Hospital, Bangalore
Bangalore, India
Dr. Sindhu Paul Kavalakkat
Consultant
Experience: 20 years of experience
Manipal Hospital (Old Airport Road) Bangalore
Bangalore, India
Dr.Pranav Chadha
Consultant
Experience: 13 years of experience
Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital Mumbai
Mumbai, India
Dr. Santanu Sen
Consultant , MBBS, MS, DNB, Fellowship, Diploma
Experience: 15 years of experience
Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital, Mumbai
Mumbai, India
Dr. Jose Easow
Consultant
Experience: 25 years of experience
Apollo Cancer Hospital, Chennai
Chennai, India