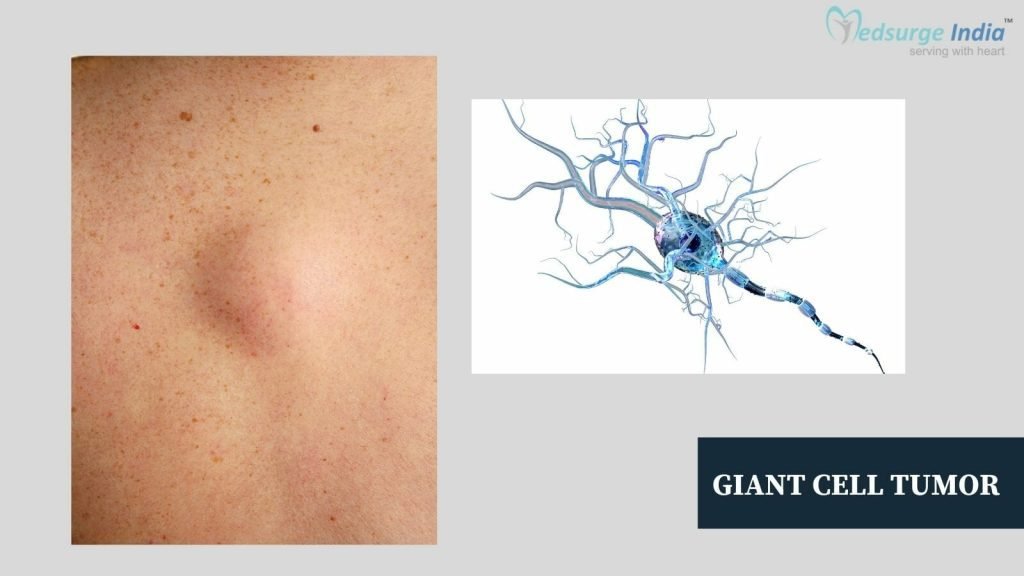
A giant cell tumor of the bone is an aggressive, rare non-cancerous tumor. The completion of skeletal bone growth typically occurs in humans between the ages of 20 and 40. It typically appears towards the end of the bone, close to a joint. Although the bones in the arms and legs can also be affected, the location of a giant cell tumor is frequently in the knee. Flat bones like the breastbone and pelvis are also susceptible. A giant cell tumor treatment in India is done by specialized orthopedic oncologists. Bone grafting is the most suitable method of treatment for a giant non-cancerous tumor.
The giant cell tumor treatment cost in India is quite affordable as compared to other European countries. The treatment cost plan depends upon the size and location of the tumor.
What Is Giant Cell?
A type of benign (noncancerous) growth is called a giant cell tumor (GCT). The majority of the time, GCTs don’t spread to other body organs because they aren’t cancer; however, they can very rarely spread to your lungs. However, because they are regarded as locally aggressive tumors, they may grow swiftly and harm nearby tissues.
At the end of one of your bones, you can develop a large cell tumor. These tumors frequently appear around the top or bottom of your thigh, or at the bottom of your thigh (femur), close to your knee (tibia). The term “tenosynovial giant cell tumor” refers to (TGCTs) that develop in soft tissues. Even while TGCTs are locally aggressive like GCTs, they are even less likely to spread.
What Are the Symptoms of a Giant Cell Tumor?
The most typical symptoms of a giant cell tumor are as follows. However, every individual may experience symptoms in a unique way. Some signs could be:
- A definite mass
- Fractured bones
- Fluid accumulation in the joint closest to the injured bone
- Limited movement in the nearest joint
- Swelling
- Discomfort at the proximal joint
- A noticeable bump
GCT symptoms affect the joint where the growth is. Usually, the first sign of a TGCT is pain or swelling around one joint. You may also have:
- Popping, catching, or locking sensations.
- Touchable skin that is soft or warm.
- Stiffness.
Your joint can start to feel unstable over time. Your cartilage may lose elasticity if you have large TGCTs. Your bones are protected and cushioned by cartilage. Arthritis develops as cartilage deteriorates over time.
What Are the Causes of Giant Cell Tumors?
The cause of giant cell tumors is unknown. The tumors develop on their own. Trauma, environmental circumstances, or food are not known to be the causes of them. Bone giant cell tumors do not run in families.
The overactivity of the parathyroid glands, or hyperparathyroidism, may also be linked to the tumors. This is different from a single, isolated bone giant cell tumor.
When your chromosomes change, GCTs developed. The primary component of your cell that houses DNA is called a chromosome. The reason for the chromosomal alteration that results in TGCT is unknown to experts.
Giant Cell Tumor Treatment Cost In India
Giant Cell Tumor Treatment Cost in India starts from USD 4500. However, the specific method of treatment used to carry out the procedure will determine the cost of your Giant Cell Tumor Treatment in India.
Below are the average cost of Giant Cell Tumor Treatment in different cities in India:
| Cities | Starting Prices |
| Delhi | USD 4500 |
| Noida | USD 4600 |
| Gurgaon | USD 4800 |
| Bangalore | USD 5000 |
| Chennai | USD 4600 |
| Kolkata | USD 4500 |
| Mumbai | USD 5000 |
| Hyderabad | USD 4700 |
Note: The price of the treatment will depend on serval factors.
Factors That Can Affect Giant Cell Tumor Treatment Cost in India
The standard of medical care and services is on par with the world’s top hospitals in terms of quality and standard. Regardless of deducting the cost of lodging, meals, and transportation. The following factors may impact giant cell tumor treatment cost in India:
- Medication costs.
- Duration of treatment.
- Geographical location.
- Hospitalization expenses.
- Government policies and subsidies.
- Medical tourism packages.
- Hospital reputation and infrastructure.
- The expertise and experience of medical professionals.
- The type and frequency of diagnostic procedures.
- The choice of treatment modality.
By being aware of these variables, patients and medical professionals can successfully negotiate and make choices that suit their requirements and preferences.
How the Diagnosis of Giant Cell Tumor is Done?
For the diagnosis of Giant cell tumor, different tests recommended by experts besides a thorough medical history and physical examination may include:
Biopsy: A test in which the presence of cancer or other abnormal cells is determined by taking tissue samples from the body and examining them under a microscope.
Radionuclide Bone Scans: A nuclear imaging test that is used to find bone cancers and disorders as well as to identify what is causing any pain or inflammation in the bones.
X-rays: A diagnostic procedure that records pictures of inside organs, bones, and tissues on film using invisible electromagnetic radiation beams.
Get Free Cost Estimation
Procedure
Giant Cell Tumor Treatment In India
Following diagnosis, treatment is typically necessary because, in the absence of treatment, a giant cell tumor will continue to develop and erode the nearby bone. The objectives of giant cell tumor treatment in India include:
- Removing tumor
- Protect the bone from injury
- Avoid recurrence of the tumor
Although surgery is the primary method for the treatment of giant cell tumors in India, there are several circumstances where this method is not safe or successful. Your doctor might advise nonsurgical treatment in this situation.
Non-Surgical Treatment May Include the Following:
Radiation Therapy:
Giant cell tumors can potentially be reduced by radiation therapy in regions where surgery may be challenging to do without damaging delicate tissues, such as the spine. Radiation therapy is only used in rare circumstances because it can result in the formation of cancer in some patients.
Tumor Embolization:
Specific arteries that supply blood to the tumor are blocked during this treatment. The tumor cells start to degenerate without their supply of oxygen and nutrients. Embolization is typically done before surgery, however, it can also be utilized on its own when surgery is not an option.
Medication:
The use of an injectable drug to treat giant cell tumors has recently been approved by the FDA. The drug targets a unique receptor on the large cells to produce its desired effects. This lessens activity and slows down bone resorption. The tumor, however, will come back after ceasing the treatment since the tumor cells are wedged between the giant cells. Sometimes the medication is used to treat recurrent cancers or situations where surgery can not be performed.
Surgical Treatment May Include the Following:
Curettage:
The surgical procedure curettage is most frequently used to treat giant cell tumors. In curettage, the tumor is scraped out of the bone using specialized tools.
Bone Graft:
After curettage, the cavity is filled with a bone graft to help stabilize the bone. A bone graft is a bone that is taken from a donor (allograft) or from another bone in your own body (autograft) — most often the hip.
To fix the hole, your doctor might also use a bone cement mixture. To try to lower the risk of recurrence, additional chemicals are frequently injected into the bone cavity, such as liquid nitrogen, hydrogen peroxide, or phenol. The risk of recurrence may occasionally be decreased with the aid of an argon gas laser.
Physical Therapy Management
Although it has no direct impact on treating the giant cell tumor itself, physical therapy management will play a significant part in the patient’s overall wellness. The physical therapist may be the first to connect the patient’s signs and symptoms to something other than musculoskeletal origin; by recognizing the warning signs that could point to giant cell tumors, the PT is able to refer the patient so they can undergo the necessary diagnostic tests to identify the tumor. This is important in order to diagnose the tumor at an early stage and take the necessary steps to remove it.
Suggestion
Giant cell tumors rarely pose a risk to life. However, they might harm your tissues and bones. See your doctor straight away if you notice any symptoms that could indicate a giant cell tumor. You might want to visit an orthopedic oncologist, who focuses on bone cancer if one is available to you.
The Most Important Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What Is the Best Treatment for Giant Cell Tumors?
A: The most successful method of treating giant cell tumors is surgery. Curettage is one surgical procedure. The surgical operation curettage is most frequently used to treat giant cell tumors.
Q: Can Giant Cell Tumors Metastasize?
A: Bone giant cell tumors can occasionally be locally aggressive and have the potential to spread, however, this is rare. We looked for relationships between clinical and histopathologic factors and metastasis, as well as between metastases and long-term outcomes and the most effective treatments.
Q: What Is a Chondroblastoma?
A: A rare variety of non-cancerous bone tumor that starts in cartilage is called chondroblastoma. Most bones are formed from this specialised, gristly connective tissue. It is crucial to the development process. The body contains a wide variety of cartilage types.
Q: What Do Giant Cells Indicate?
A: Various cells, including macrophages, epithelioid cells, monocytes, etc., fuse to generate giant cells, which are multi-nucleated, huge in size, and frequently found near the site of chronic inflammation and other granulomatous diseases.
Top Hospitals for Giant Cell Tumor Treatment In India
Top Doctors for Oncology and Oncosurgery
Dr. Atul Srivastava
Senior Consultant
Experience: 15 years of experience
Medeor Hospital, Qutab, New Delhi
New Delhi, India
Dr. Neelesh Reddy
Consultant
Experience: 23
Manipal Hospital Formerly Columbia Asia Referral Hospital, Bangalore (Yeshwanthpur)
Dr. Yogesh Kulkarni
Consultant , MBBS, MD, DNB, Fellowship
Experience: 17 years of experience
Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital, Mumbai
Mumbai, India
Dr. Vijay Agarwal
Senior Consultant , Diploma, MRCP, MD, MBBS
Experience: 17 years of experience
Aster CMI Hospital (Hebbel) Bangalore
Bangalore, India
Dr. Praveen K. Dadireddy
Consultant , MBBS
Experience: 18 years of experience
Continental Hospitals, Hyderabad
Hyderabad, India
Dr. Bhawana Saddy Awasthy
Senior Consultant
Experience: 20 years of experience
Marengo Asia Hospitals Formerly W Pratiksha Hospital, Gurgaon
Gurgaon, India
Dr. Sudeep Sarkar
Senior Consultant
Experience: 35 years of experience
Nanavati Super Specialty Hospital Mumbai
Mumbai, India
Dr. Rajkumar Prakash
Experience: 10+ years of experience
Narayana Superspeciality Hospital, Amingaon, Guwahati
Guwahati, India
Dr. Kanika S
Associate Consultant
Experience: 15 years of experience
Max Superspecialty Hospital, Mohali
Mohali, India
Dr. Senthil Kumar
Consultant , MBBS, MS, MCh, Fellowship
Experience: 14 years of experience
Chennai, India
Dr. Kanika Rana
Associate Consultant
Experience: 10 years of experience
Medanta – The Medicity, Gurgaon
Gurgaon, India
Dr. B Krishnamoorthy Reddy
Senior Consultant
Experience: 30 years of experience
Apollo Hospital Bangalore Bannerghatta Road
Bangalore, India
Dr Sivaram G
Consultant
Experience: 18 years of experience
Apollo Cancer Hospital, Chennai
Chennai, India
Dr. Kalaichelvi
Consultant
Experience: 24 years of experience
Apollo Cancer Hospital, Chennai
Chennai, India