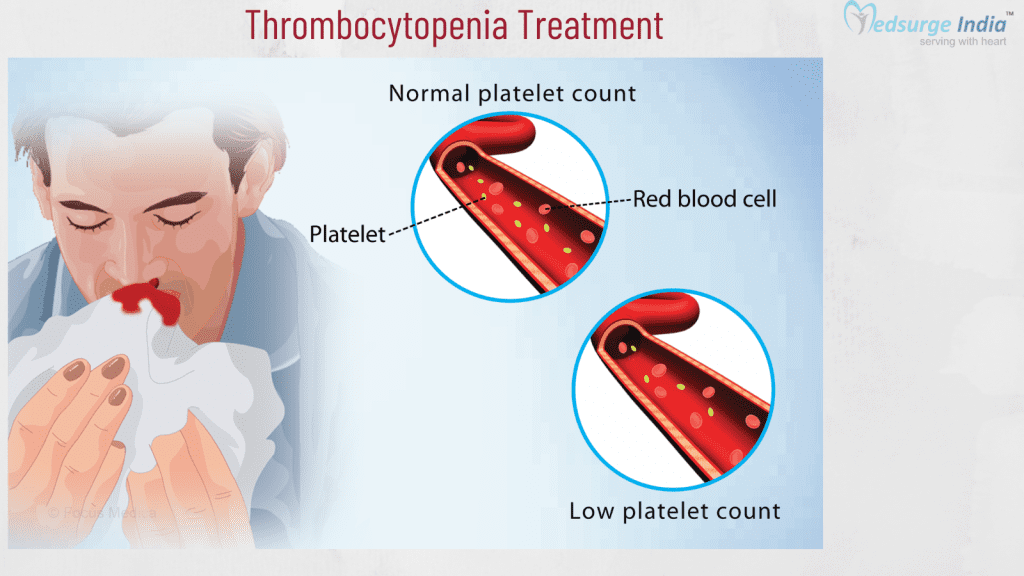
Platelet levels are low in people with thrombocytopenia. Platelets help in blood clotting (stop bleeding). You may bruise and bleed excessively if your platelet levels are low. The condition can be caused by certain cancers, cancer treatments, medications, and autoimmune diseases. When the underlying cause is addressed, platelet levels frequently improve. For thrombocytopenia treatment in India, doctors may prescribe medications, recommend blood or platelet transfusions, and, in rare cases, a splenectomy to remove the spleen partially or completely.
Because thrombocytopenia is a blood disorder, only a hematologist can treat it. A complete blood count (CBC) test, which involves taking blood from a blood vessel in the arm, reveals the existence of thrombocytopenia.
In comparison to other countries, the cost of thrombocytopenia treatment in India is low. The total cost of treating a patient with low platelets may depend on various transitional factors. This treatment is widely available in almost all hospitals across India.
What Is Thrombocytopenia?
When your blood platelet count is low, you have thrombocytopenia. Platelets are also referred to as thrombocytes. This type of blood cell clumps together to form blood clots, which help in the halting of blood at the site of a cut or wound. A blood clot is also known as a thrombus.
The soft, spongy tissue inside bones that produces all blood cells, including platelets, is known as bone marrow. Thrombocytopenia occurs when a person’s platelets are grossly inadequate to form a blood clot. If you get a cut or another type of injury, you may bleed excessively, which can be difficult to stop.
There are three types of thrombocytopenia:
- Platelet destruction, such as with an auto-antibody that binds to the platelet surface.
- Platelet sequestration, as in someone with a large spleen or liver disease.
- Platelet production is reduced in bone marrow diseases.
People of all ages, races, and genders can be affected by thrombocytopenia. Approximately 5% of pregnant women develop mild thrombocytopenia right before childbirth for unknown reasons. Thrombocytopenia can be caused by a bone marrow disorder like leukemia or an immune system disorder. It could also be a side effect of certain medications. It has an impact on both children and adults.
Thrombocytopenia can be mild, resulting in few signs and symptoms. In rare cases, the platelet count can fall so low that dangerous internal bleeding occurs. There are treatment options available.
What Are the Symptoms of Thrombocytopenia?
The severity of the symptoms of thrombocytopenia is usually determined by the underlying cause and can range from mild to severe. Some people may not experience serious symptoms, whereas others may experience severe bleeding, which can be fatal if not treated promptly.
Low platelet count symptoms include:
- Gum bleeding
- Blood in the faeces or urine
- Heavy menstrual flow
- Vomiting of blood
- Bleeding in the rectum
- Internal bruising
- Rashes with red or purple dots known as Petechiae
- Red, brown, or purple bruise marks also known as Purpura
- Even more serious symptoms, such as brain bleeding can occur
- Fatigue
- Enlarged Spleen
Make an appointment with your doctor if you notice any thrombocytopenia symptoms. Bleeding that won’t stop is a medical emergency. Seek immediate assistance if bleeding cannot be controlled using standard first-aid techniques, such as applying pressure to the area.
What Are the Causes of Thrombocytopenia?
Thrombocytopenia can be inherited or passed down from parent to child in rare cases. A low platelet count is more commonly caused by certain disorders, conditions, and medications. These are some instances:
- Alcoholism and alcohol use disorder
- ITP is caused by an autoimmune disease. ITP is sometimes linked to other autoimmune diseases such as lupus.
- Aplastic anemia, leukemia, certain lymphomas, and myelodysplastic syndromes are all examples of bone marrow diseases.
- Different cancer treatments like chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
- Cirrhosis of the liver, also known as Gaucher disease, causes an enlarged spleen. Platelets and other blood cells are trapped in the enlarged spleen, preventing them from circulating in the bloodstream.
- Toxic chemical exposure, such as arsenic, benzene, and pesticides.
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections, epilepsy, and heart problems, as well as the blood thinner heparin.
- Viruses like hepatitis C, CMV, EBV, and HIV
Thrombocytopenia Treatment Cost in India
Thrombocytopenia Treatment Cost in India starts from USD 4,500. Here are the estimated prices depending on different cities in India.
Thrombocytopenia Treatment Cost in Different Parts of India
| Cities | Starting Price |
| Delhi | USD 4500 |
| Gurgaon | USD 4500 |
| Noida | USD 4500 |
| Mumbai | USD 4700 |
| Hyderabad | USD 4500 |
| Chennai | USD 4500 |
| Kolkata | USD 4500 |
| Bangalore | USD 4700 |
Please keep in mind that prices of Thrombocytopenia Treatment Cost in India will vary depending on various factors.
Factors That Can Affect Thrombocytopenia Treatment Cost in India
The following here are some variables that can affect Thrombocytopenia Treatment Cost in India:
- Medication costs.
- Duration of treatment.
- Geographical location.
- Hospitalization expenses.
- Government policies and subsidies.
- Medical tourism packages.
- Hospital reputation and infrastructure.
- The expertise and experience of medical professionals.
- The type and frequency of diagnostic procedures.
- The choice of treatment modality.
The standard and grade of medical care and amenities are comparable to those of the most prestigious healthcare facilities in the world, even when the expense of lodging, meals, and transportation is taken out. Under the direction of the most skilled physicians, Medsurge India provides patients with the lowest Thrombocytopenia Treatment Cost in India.
How Is Thrombocytopenia Diagnosed?
If you have difficult-to-stop bleeding or other signs of thrombocytopenia, your healthcare provider may do the following:
- Physical examination: The healthcare provider will go over your family and medical history. You’ll talk about the medications you’re taking. In addition, your doctor will look for bruises, rashes (petechiae), and an enlarged spleen or liver.
- Blood count: A complete blood count (CBC) measures platelet, white and red blood cell levels.
- Blood clot test: It determines how long it takes blood to clot. The partial thromboplastin time (PTT) and prothrombin time (PT) are two of these tests (PT).
If your platelet count is low, your doctor may order additional tests to determine the causes of thrombocytopenia, such as:
- Biopsy of bone marrow: Taking a sample of bone marrow can aid in the diagnosis of bone marrow diseases or cancer.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound or CT scans can detect an enlarged spleen, enlarged lymph nodes, or liver cirrhosis.
Get Free Cost Estimation
Procedure
How is Thrombocytopenia is Managed or Treated?
Thrombocytopenia can last from a few days to several years. Mild thrombocytopenia may not require treatment. Treatment for thrombocytopenia in India is dependent on the cause and severity of the condition.
If your thrombocytopenia is caused by an underlying condition or a medication, treating the underlying condition or medication may cure it. If you have heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, your doctor may prescribe a different blood-thinning medication.
Other treatments may include:
- Transfusions of blood or platelets: If your platelet count falls below a certain threshold, your doctor may replace lost blood with transfusions of packed red blood cells or platelets.
- Medication: If your condition is caused by an immune system problem, your doctor may prescribe medications to increase your platelet count. A corticosteroid may be the first-line treatment. If that doesn’t work, stronger medications to suppress your immune system can be used.
- Surgery: If other treatments fail, your doctor may advise you to have your spleen removed (splenectomy).
- The exchange of plasma: Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura can cause a medical emergency that necessitates plasma exchange.
If the symptoms of a low platelet count are not severe enough, the doctor will not treat the patient and will allow the condition to heal on its own. However, if the symptoms are severe, treatment for this problem becomes necessary.
Patients with low platelet counts are frequently advised to avoid contact sports and other jobs that pose a high risk of bleeding, to consume less alcohol, and to discontinue or change medications that have a negative impact on platelet count.
Helpful – Bone Marrow Cancer Treatment Cost In India
What Are the Possible Risks and Complications Associated with Thrombocytopenia?
People suffering from severe thrombocytopenia are at risk of significant internal and external blood loss, also known as hemorrhage. Internal bleeding into the gastrointestinal tract or brain (intracranial hemorrhage) can be fatal. A splenectomy increases your susceptibility to infections. The spleen is a component of your immune system. It aids your body’s defense against germs. As a result, patients who must have their spleen removed are given a series of vaccinations to help prevent infection.
How Can I Prevent Thrombocytosis?
If you are at risk for thrombocytopenia, the following steps may help you avoid it:
- Aspirin, Naprosyn, and Ibuprofen are examples of medications that thin the blood and increase the risk of bleeding.
- Avoid contact sports and activities that can result in injuries, bruising, and bleeding.
- Reduce your exposure to toxic chemicals.
- When shaving, brushing your teeth, and blowing your nose, use extra caution.
- Limit your intake of alcohol, which slows platelet production and causes liver damage.
Suggestion
When the underlying cause of platelet deficiency is addressed, the problem of low blood platelets is frequently resolved. However, post-treatment guidelines for such patients include eating a healthy diet rich in vegetables and fruits, avoiding foods containing quinine and aspartame, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and avoiding contact sports or other activities that pose a high risk of bleeding or injury.
Furthermore, patients are advised not to take medications such as aspirin and ibuprofen because they lower the count of blood platelets and make bleeding easier. If a patient experiences any side effects from the treatment, he or she should immediately consult a doctor for treatment options.
The Most Important Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is Thrombocytopenia Associated with a Long Life?
A: The most common form of ITP is acute ITP. Thrombocytopenic purpura (chronic). The disorder can strike at any age, and the symptoms can last for 6 months, several years, or a lifetime. This form is more common in adults than in children, but it does affect adolescents.
Q: How Long Does Thrombocytopenia Treatment Take?
A: Thrombocytopenia can last from a few days to several years. Mild thrombocytopenia may not require treatment. Treatment for thrombocytopenia is dependent on the cause and severity of the condition.
Q: Can Low Platelets Be Restored?
A: It is essential to determine the cause of low platelets. When the underlying cause is identified, treatment can usually help your levels return to normal. A platelet transfusion may be required in some cases.
Q: What Is the Most Effective Treatment for Low Platelets?
A: If your low platelet count is severe, you may require medical attention. Blood or platelet transfusions may be used as a treatment option. modifying medications that cause a low platelet count.
Q: Who Is at Risk of Developing Thrombocytopenia?
A: Young women are more likely to have ITP. People who have rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, or antiphospholipid syndrome appear to be at a higher risk.
Top Hospitals for Thrombocytopenia Treatment in India
Top Doctors for Bone Marrow and Hematology
Dr. Rahul Bhargava
HOD
Experience: 17 years of experience
Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurgaon
Gurgaon, India
Dr. Anil Handoo
HOD
Experience: 10 years of experience
BLK Super Speciality Hospital, New Delhi
New Delhi, India
Dr. Kishore Kumar S
Senior Consultant , MBBS, DM, MD
Experience: 14 years of experience
Chennai , India
Dr. Shobha Badiger
Consultant
Experience: 18 years of experience
Rajarajeshwari Medical College, Bangalore
Bangalore, India
Dr. Ujal Mani
Senior Consultant
Experience: 42+ years of experience
NH Rabindranath Tagore International Institute of Cardiac Sciences, Kolkata
Kolkata, India
Dr. Gaurav Kharya
Senior Consultant , MBBS, DCH, DNB, Fellowship
Experience: 18 years of experience
Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, New Delhi
New Delhi, India
Dr. Satish Kumar A
Consultant
Experience: 24 years of experience
Manipal Hospital Formerly Columbia Asia Referral Hospital, Bangalore (Yeshwanthpur)
Bangalore, India
Dr. Meet Kumar
Hematologist Consultant, MBBS, MD, DM, Fellowship
Experience: 11 years of experience
Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurgaon
Gurgaon, India
Dr. Vikas Dua
Senior Consultant
Experience: 23 years of experience
Fortis Memorial Research Institute
Gurgaon, India
Dr. Prathamesh Kulkarni
Consultant
Experience: 9 years of experience
Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital Mumbai
Mumbai, India
Dr. Sarmila Chandra
Senior Consultant
Experience: 25+ years of experience
NH Rabindranath Tagore International Institute of Cardiac Sciences, Kolkata
Kolkata, India
Dr. Chezhian Subash
Consultant , MBBS, MRCP, FRCP
Experience: 25 years of experience
Chennai , India
Dr. Shyam Rathi
Consultant
Experience: 14 years of experience
Fortis Hiranandani Hospital, Vashi
Mumbai, India
Dr. Aniruddha Purushottam Dayama
Chief
Experience: 15 years of experience
Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurgaon
Gurgaon, India
Dr. Riya Balilkar
Consultant
Experience: 10 years of experience
Wockhardt Super Speciality Hospital Nagpur
Kolkata, India